The existence of dark matter, which makes up approximately 80% of the universe, continues to baffle astrophysicists due to its elusive nature. Unlike ordinary matter, dark matter does not emit, reflect, or absorb light, making it undetectable through traditional experimental methods. The quest to unravel the secrets of dark matter has led physicists worldwide to explore innovative techniques to identify and understand this elusive component of the cosmos. One such initiative is the Broadband Reflector Experiment for Axion Detection (BREAD), a groundbreaking research project spearheaded by physicists from the University of Chicago and the Fermi Accelerator Laboratory.
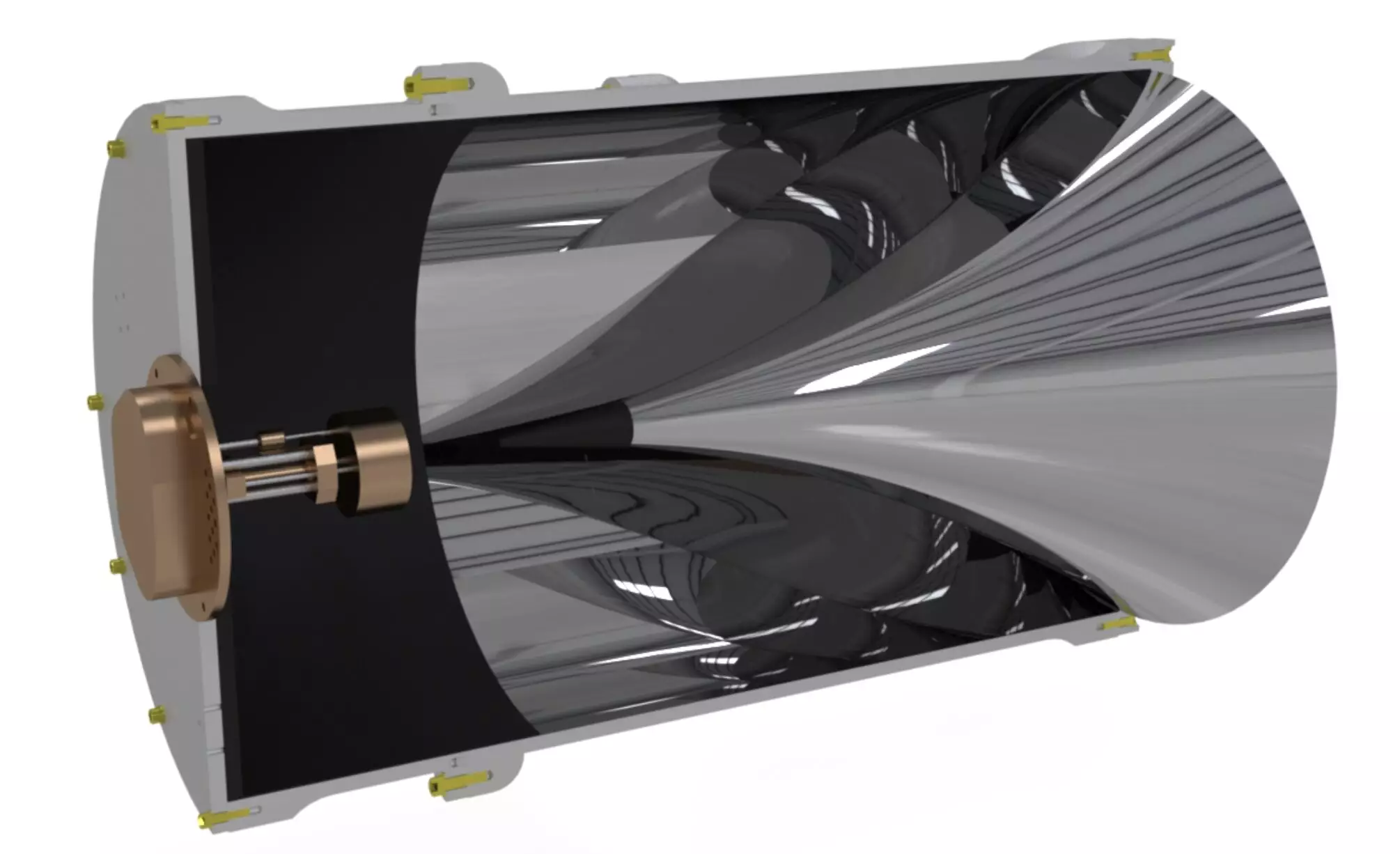
The BREAD Collaboration introduces a novel approach to the search for light dark matter candidates, such as dark photons and axions. Through the utilization of a coaxial dish antenna, the BREAD project aims to capture signals associated with these elusive particles. Stefan Knirck, the corresponding author for the BREAD Collaboration, highlights the significance of exploring alternative avenues to identify the mysterious substance surrounding us. By focusing on the dark photon and the axion as potential candidates for dark matter, the BREAD project opens up new possibilities in the field of particle astrophysics.
Dark photons and axions, theorized to be significantly lighter than protons, present a unique challenge in terms of detection. The BREAD Collaboration’s groundbreaking technology offers a promising solution to this challenge by focusing on detecting these lighter particles. In their initial small-scale experiment, the researchers investigate the conversion of dark matter into light particles on a metallic wall, showcasing the innovative design of the experiment. The integration of a magnetic field in future iterations of the experiment further enhances its sensitivity to axion dark matter, setting the stage for groundbreaking discoveries in the field.
The BREAD Collaboration’s recent data collection efforts between June and July 2023 yielded valuable insights into the detection of dark photons. While the initial results did not yield any significant signals, the experiment showcased a remarkable increase in sensitivity compared to previously proposed methods. The researchers remain optimistic about the potential of their approach, emphasizing the need for continued development and scaling of the technology to enhance its sensitivity and expand the range of detectable dark matter masses.
The BREAD Collaboration’s innovative approach holds the key to exploring the most compelling axion models and potentially unlocking the mysteries of dark matter. By conducting experiments in high-field solenoid magnets and integrating cutting-edge quantum technology, the researchers are paving the way for unprecedented discoveries in the field of particle astrophysics. As they continue to push the boundaries of scientific exploration, the BREAD Collaboration remains dedicated to enhancing the sensitivity of their experiments and unraveling the enigmatic nature of dark matter.
The BREAD Collaboration’s pioneering research serves as a beacon of hope in the quest to uncover the secrets of dark matter. Through their innovative approach and groundbreaking technology, the researchers are poised to revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos and shed light on the mysterious substance that dominates the universe. As they continue to push the boundaries of scientific discovery, the BREAD Collaboration inspires future generations of physicists to explore the unknown and unravel the complexities of the universe.

Leave a Reply