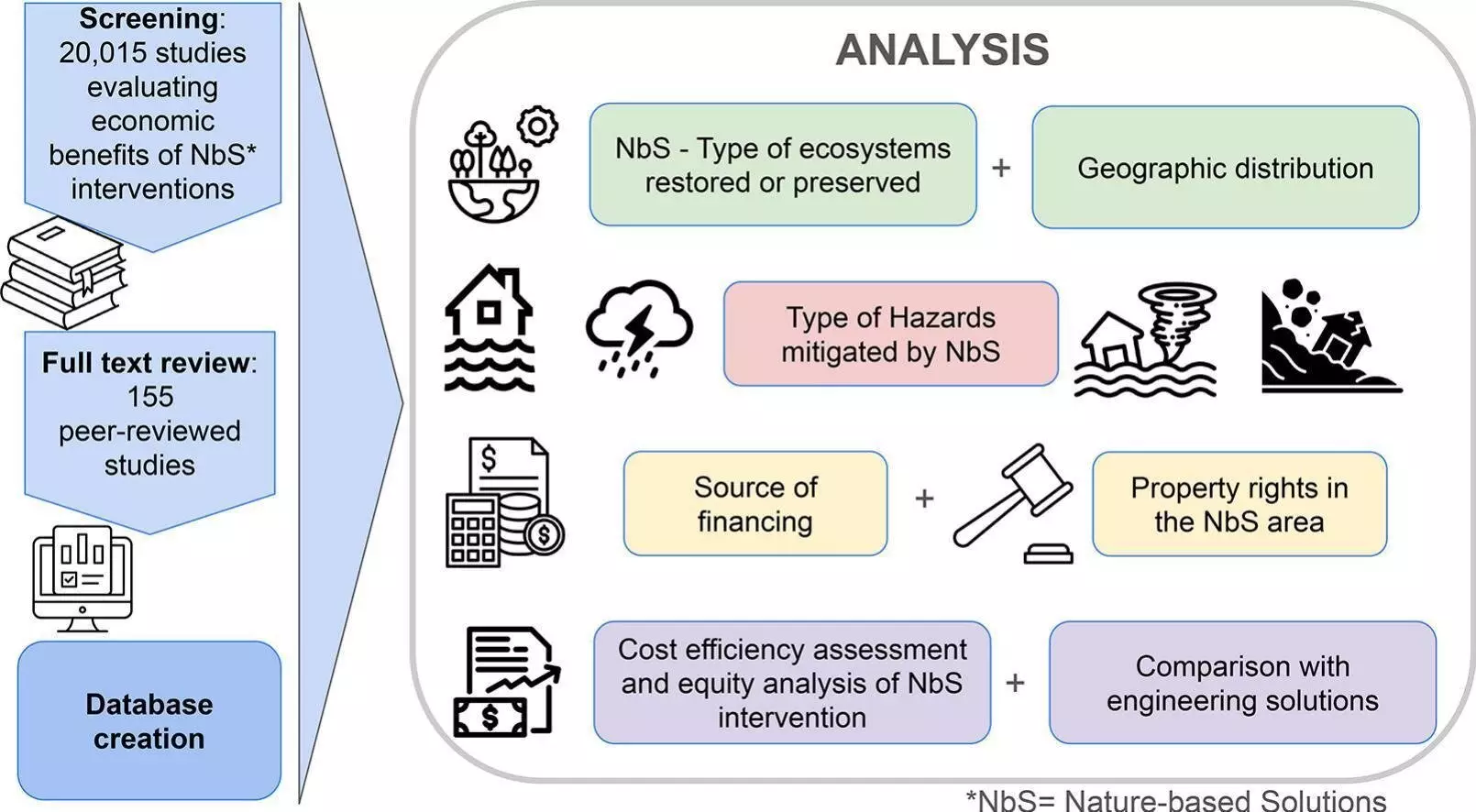
As the world grapples with the increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters due to climate change, the importance of nature-based solutions (NbS) cannot be overstated. A recent global assessment led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst highlights the economic effectiveness of NbS in mitigating risks associated with a wide range of disasters, including floods, hurricanes, heat waves, and landslides. These interventions involve the preservation, sustainable management, or restoration of ecosystems to provide benefits to both society and nature. While traditional engineering-based solutions have long been the go-to approach, NbS offer a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative.
The study found that NbS are consistently cost-effective in mitigating hazards in 71% of the more than 20,000 peer-reviewed studies analyzed. Additionally, 24% of the studies deemed NbS cost-effective under certain conditions. Mangroves, forests, and coastal ecosystems were identified as the most effective ecosystem-based interventions for hazard mitigation. Furthermore, when compared to engineering-based solutions, NbS were found to be more effective in 65% of the cases and equally effective in 24% of the cases. Notably, no study concluded that NbS were less effective than engineering solutions.
Despite the proven effectiveness of NbS in hazard mitigation, the study also uncovered a significant underestimation of their additional environmental and socioeconomic benefits. Many studies failed to consider the broader advantages of NbS, such as biodiversity conservation, climate mitigation, and support for marginalized communities. The value of improvements in air quality, soil quality, protection of endangered species, and overall increase in biodiversity remains difficult to quantify. As a result, these added benefits are often overlooked and undervalued in the assessment of NbS effectiveness.
One of the key findings of the research is the reliance on public sector funding for NbS implementation, even in cases involving private property. To truly maximize the impact of NbS on a global scale, a more diversified funding approach is essential. The researchers emphasize the importance of increased private sector investment in NbS to catalyze transformative change. While public financing has played a crucial role in supporting NbS initiatives, a significant influx of private capital is needed to accelerate the adoption of nature-based solutions worldwide.
The assessment of nature-based solutions offers valuable insights into their economic effectiveness and potential to mitigate a wide range of hazards. While NbS have gained recognition in national and international climate policies, there is still room for improvement in capturing and valuing their full range of benefits. Moving forward, a more holistic approach to assessing the impact of NbS, coupled with diversified funding sources, will be crucial in harnessing the power of nature-based solutions to combat climate change and protect ecosystems for future generations.

Leave a Reply