Rice University chemist James Tour and his research team have made significant progress in the field of soil remediation with the development of the Rapid Electrothermal Mineralization (REM) process. This innovative technique aims to tackle the accumulation of synthetic chemicals, specifically per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which pose a threat to the environment and human health.
Traditional methods used for breaking down PFAS in soil often prove to be inefficient, consuming large amounts of energy and water without completely eliminating the contaminants. This is where the REM process shines, offering a faster, more efficient, and environmentally friendly solution to soil remediation.
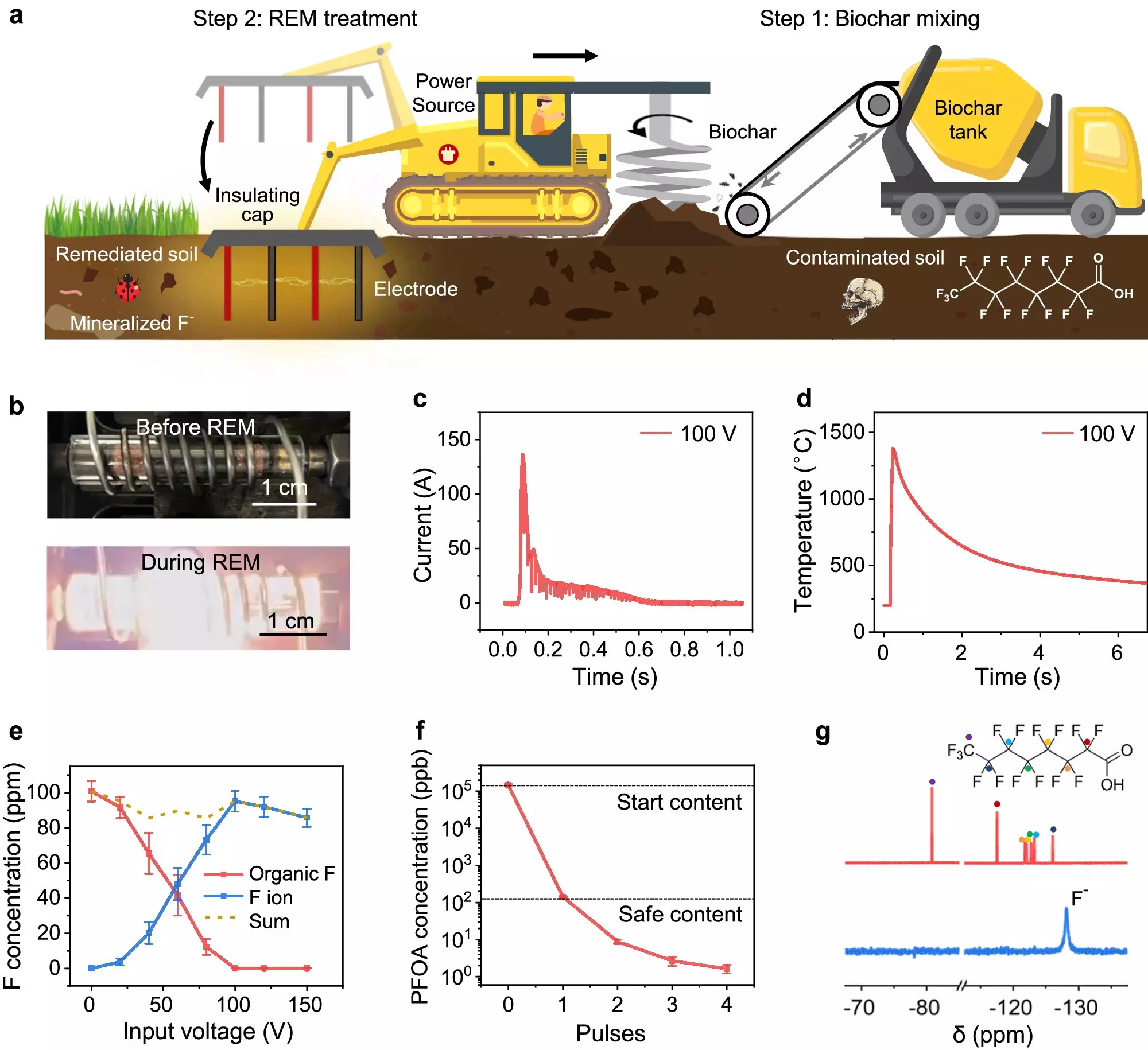
The REM process involves the use of electrical inserts in the ground along with biochar, an environmentally friendly conductive additive. By rapidly heating contaminated soil to over 1,000°C in a matter of seconds through a direct current pulse, the intense heat effectively converts PFAS into calcium fluoride, a harmless mineral. This method has shown to achieve high removal efficiencies and mineralization ratios of over 90%.
Not only does the REM process effectively mineralize PFAS into non-toxic substances, but it also helps retain essential soil properties and improve soil health. By enhancing nutrient supply and supporting the infiltration of arthropods, this breakthrough in soil remediation provides a holistic approach to environmental conservation.
One of the key advantages of the REM process is its minimal environmental impact. By reducing energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and water usage compared to traditional methods, this technique presents a more sustainable approach to soil remediation. Furthermore, the scalability of the REM process allows for larger-scale application systems to be designed, making it a practical solution for widespread use.
The development of the REM process marks a significant milestone in the field of soil remediation. By combining efficiency, speed, and environmental benefits, this innovative technique offers a more sustainable and cost-effective approach to addressing soil contamination. With further advancements and application on a larger scale, the REM process has the potential to become a game-changer in environmental conservation efforts.

Leave a Reply