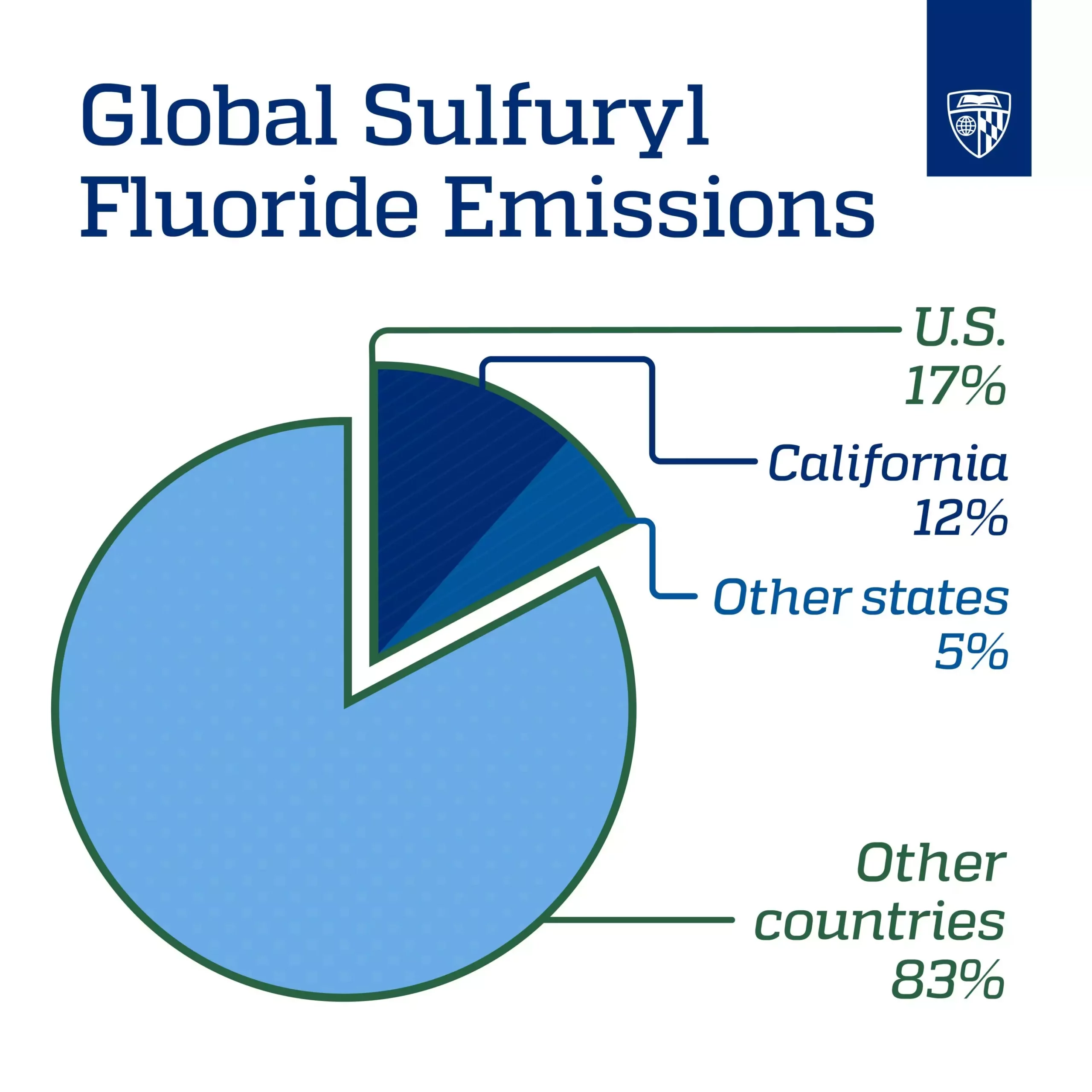
California, a state widely recognized for its progressive climate policies and efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, has found itself in a rather ironic situation. Despite being at the forefront of environmental initiatives, particularly in aiming for net-zero emissions by 2045, California is actually the largest emitter of sulfuryl fluoride in the United States. This gas, commonly used as a pesticide for tackling termites and other wood-infesting insects, accounts for as much as 17% of global emissions of this harmful substance, with the majority of these emissions concentrated in just a few counties within the state.
A recent study conducted by Johns Hopkins University shed light on this unexpected revelation. By analyzing over 15,000 air samples collected between 2015 and 2019, researchers were able to pinpoint the origins of sulfuryl fluoride emissions in the U.S. The study, published in Communications Earth & Environment, revealed that a striking 60-85% of these emissions come from California, predominantly from counties such as Los Angeles, Orange, and San Diego. Despite California’s commendable efforts in reducing greenhouse gas emissions overall, the prevalence of sulfuryl fluoride emissions in these specific regions poses a unique challenge.
The study attributed a significant portion of California’s sulfuryl fluoride emissions to structural fumigation practices. Structural fumigation involves sealing off an infested building with an airtight tent, fumigating the space with gas to eliminate pests, and subsequently releasing the gas into the atmosphere. This method, commonly used in addressing drywood termite infestations, accounts for around 85% of the state’s sulfuryl fluoride emissions. The remainder comes from agricultural and commodities fumigation, adding to the overall environmental burden posed by this gas.
Once released into the atmosphere, sulfuryl fluoride can persist for more than 40 years, contributing to the greenhouse effect and exacerbating global warming. While the average concentrations of this gas may be low, the cumulative impact of sustained emissions is substantial. Unlike other greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane, sulfuryl fluoride has gone largely unnoticed in emission reduction strategies, highlighting the need for a more comprehensive approach to addressing different types of pollutants.
The researchers behind the study emphasized the importance of recognizing the diverse sources of greenhouse gas emissions and developing targeted strategies to mitigate their impact. While the focus has traditionally been on carbon emissions due to their primary role in driving climate change, other gases such as sulfuryl fluoride demand attention as well. Finding a balance between effective pest control measures and environmental responsibility is crucial in devising sustainable solutions to reduce emissions.
The findings of the study were shared with relevant environmental agencies in California, including the California Air Resources Board and the Bay Area Air Quality Management District. By engaging in dialogue with key stakeholders and decision-makers, researchers hope to catalyze meaningful action towards reducing sulfuryl fluoride emissions and promoting a more holistic approach to greenhouse gas reduction strategies. Through collaboration and continued research, California and other regions facing similar challenges can work towards a cleaner, greener future for all.

Leave a Reply