The Earth’s atmosphere is rich in nitrogen, crucial for the production of ammonia – a necessary component in agriculture. Traditionally, the conversion of dinitrogen gas (N2) to ammonia (NH3) has been energy-intensive and environmentally harmful. However, scientists have been exploring the use of sunlight as an alternative energy source for this process, which could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
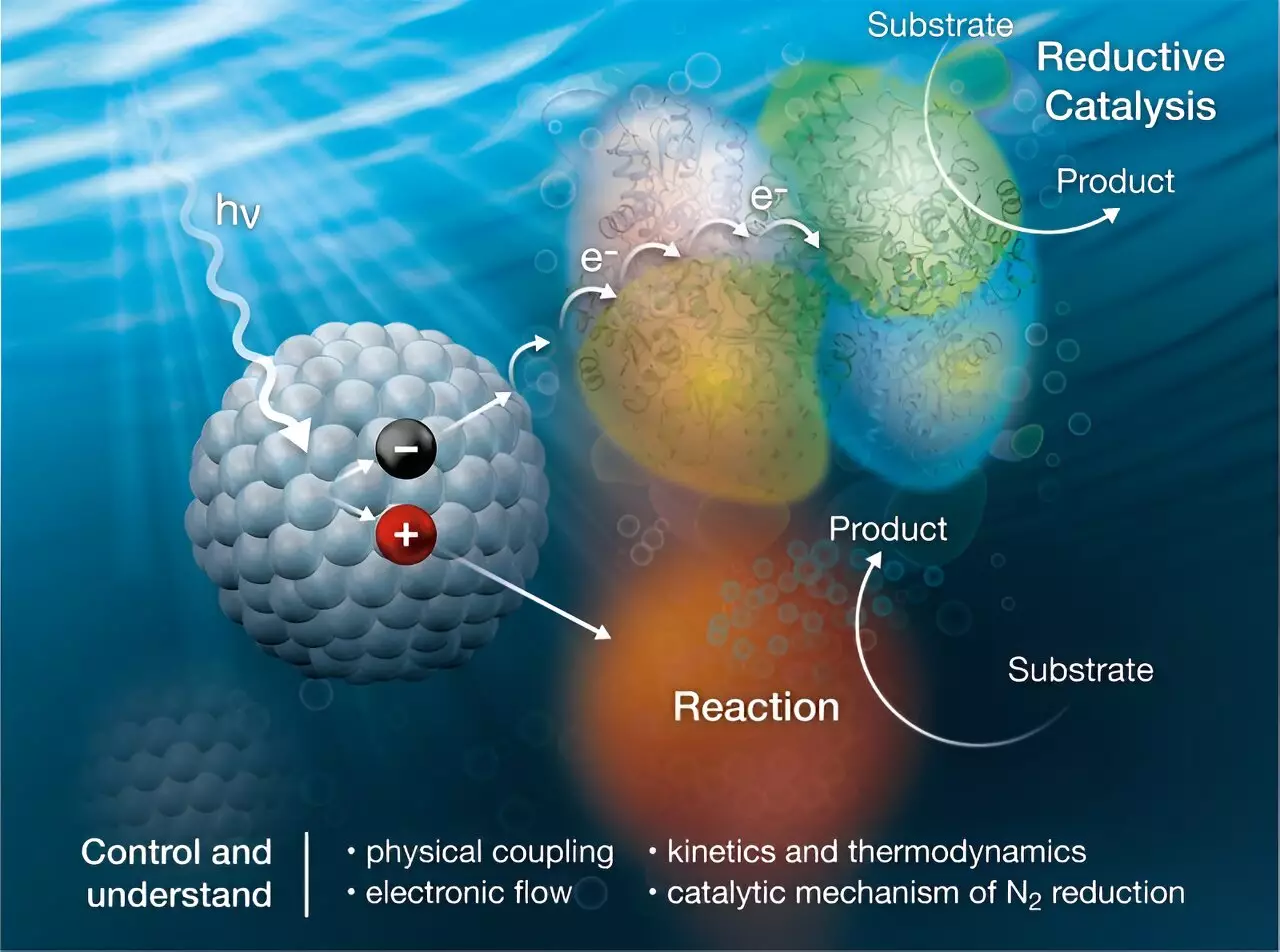
In a breakthrough study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, researchers have developed a biohybrid system that combines nanocrystals with the nitrogenase enzyme. The nanocrystals harness sunlight energy and transfer charge to the enzyme, facilitating the conversion of nitrogen to ammonia. This innovative approach not only reduces the energy requirements for ammonia production but also eliminates the production of carbon dioxide – a major greenhouse gas.
While this new sunlight-based process shows great promise, there are still challenges to be overcome. The compatibility between the nanocrystals and the enzyme, as well as the stability of the reaction complex, are crucial factors that need to be carefully studied and optimized. By understanding how to effectively couple sunlight with the ammonia production reaction, researchers can unlock the full potential of this innovative approach.
Through the development of the nanocrystal/enzyme system, scientists have made significant progress in understanding the mechanisms of ammonia production using sunlight. By studying the reaction intermediates in detail, researchers can gain valuable insights into the activation energies and kinetics of the conversion process. This foundational research is paving the way for the development of more efficient and sustainable methods for producing ammonia.
The implementation of sunlight-based processes for ammonia production could revolutionize the agricultural industry. By producing NH3 fertilizers close to where they are needed, the need for shipping and the associated carbon emissions can be significantly reduced. This not only benefits the environment but also makes the production and distribution of fertilizers more sustainable and cost-effective.
The utilization of sunlight as an energy source for ammonia production represents a major advancement in the field of chemistry. By harnessing the power of nanocrystals and enzymes, researchers have the potential to transform a traditionally energy-intensive and environmentally harmful process into a sustainable and eco-friendly solution. Through continued research and innovation, the future of agriculture and environmental sustainability looks brighter than ever.

Leave a Reply