In our increasingly mechanized world, small electric motors play a critical role in the functioning of everyday devices. These motors, compact and efficient, are embedded in various household appliances, power tools, and even sophisticated automobiles, where they manage auxiliary systems like pumps and fans. Although each individual motor may only draw a small amount of energy, their collective usage can lead to substantial energy consumption. Recognizing this potential for optimization, researchers have begun to actively explore ways to enhance the efficiency and functionality of these small electric motors.
A pioneering research initiative, led by Annette Mütze at the Graz University of Technology, has been focusing on the potential of brushless integrated drives, particularly for pumps and fans. Operating under the auspices of the CD Laboratory for Brushless Drives, the team has made significant strides in reducing energy consumption and improving overall motor performance through innovative designs and modern manufacturing techniques. These advancements herald a potential shift in how small electric motors are perceived — from mere energy consumers to optimized devices that promote sustainability.
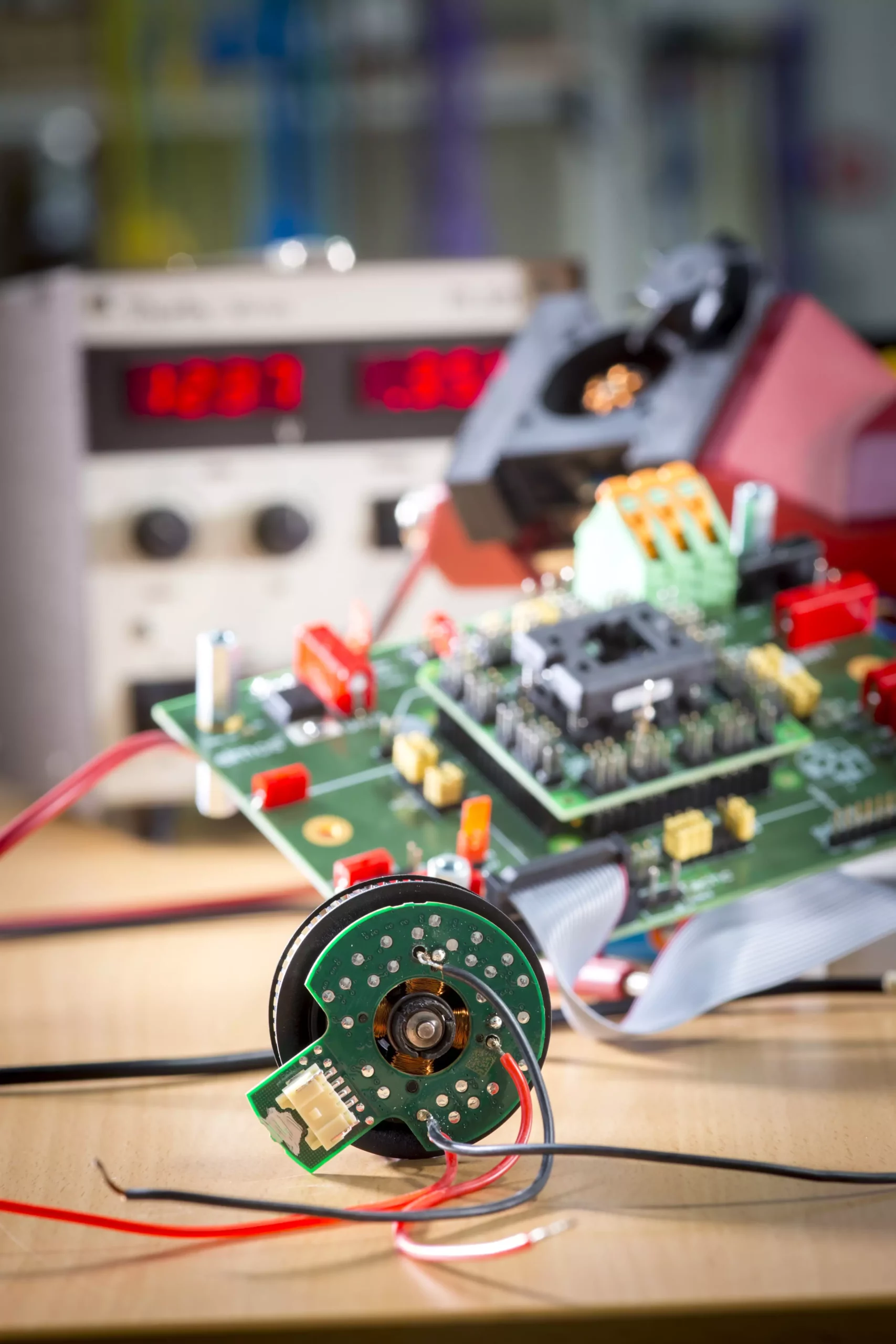
One noteworthy aspect of the team’s research involves addressing the issue of cogging torque in claw pole motors. Traditionally used in vehicle lighting, these motors have an often-overlooked application as small drive units. Mütze’s team ingeniously modified the motor’s design through a technique of skewing and slotting in the claws, thereby mitigating cogging torque without incurring additional costs. As a result, the unwanted vibrations typically associated with motor operation have been significantly reduced, leading to a 70% decrease in noise levels. This breakthrough not only enhances user experience but also contributes to a more harmonious integration of technology into our daily lives.
Efficiency optimization doesn’t stop at the mechanical design; it extends into the realm of electrical regulation. Traditional pulse width modulation (PWM) methods for controlling motor currents often involve numerous switching operations, which lead to increased energy consumption. Mütze’s team proposed a novel approach wherein their integrated drives require only a single switch-on and switch-off per desired current waveform, effectively minimizing energy loss due to switching. This innovative regulation scheme particularly shines at low current levels, where it offers a notable improvement in overall efficiency compared to traditional methods.
Furthermore, the research team’s redesign has led to a significant reduction in the number of capacitors required on the circuit boards of these motors, thereby lowering manufacturing costs. This efficiency not only simplifies production processes but also contributes to affordability, making energy-efficient motors accessible to a broader array of consumers and industries.
Another groundbreaking advancement is the introduction of PCB motors with ferrite cores, which embodies a holistic approach to innovation. By integrating the windings for the magnetic field into the design of the printed circuit boards, Mütze’s team has paved the way for high levels of automation in manufacturing. The enhancement of magnetic flux guidance through the addition of 3D-printed ferrite cores further underscores the ingenuity of this approach, enabling the use of more economical magnets without sacrificing performance.
As we continue to confront the challenges of energy consumption in our everyday lives, the technological advancements emerging from the research lab under Annette Mütze represent a promising stride towards sustainability. The innovations in brushless integrated drives not only enhance efficiency and reduce costs but also offer a tangible step forward in minimizing our environmental impact. By recalibrating our approach to small electric motors, we can harness their true potential, setting the stage for a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand. This evolution might very well define the next generation of energy-efficient appliances and tools in our homes and industries.

Leave a Reply