In a recent study published in the journal PNAS Nexus, researchers shed light on how social media algorithms contribute to favoring politically sponsored content from certain parties over others, even when given the same investment budget. The study, a collaboration between the Politecnico di Milano, LMU—Ludwig Maximilians Universität of Munich, and the CENTAI institute of Turin, focused on analyzing over 80,000 political ads on Facebook and Instagram prior to the 2021 German federal elections.
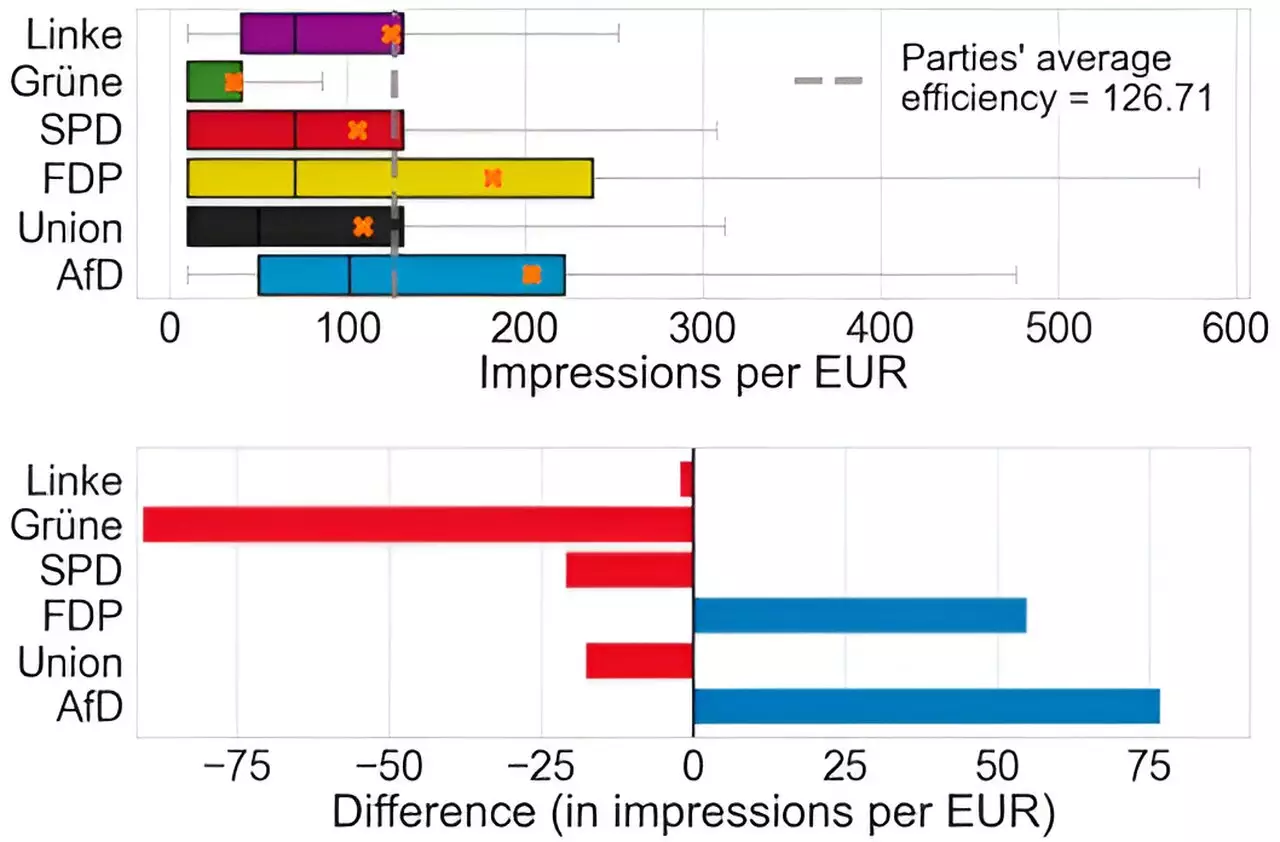
The research revealed significant discrepancies in the effectiveness of advertising and the reach of ads, particularly favoring more extremist political parties. It was discovered that over 70% of parties utilized user profiling in their ads, with variations in advertising costs showing that not all parties achieved the same results with equal budgets. The far-right AfD was found to be the most effective in terms of ad efficiency, while the Greens were the least cost-effective party. Researchers attributed the success of more extremist parties to the attention-grabbing nature of their content on social media platforms, which led algorithms to favor their campaign ads.
One concerning finding of the study was the discrepancies between the targeted audience and the actual audience reached by political ads. While most parties tended to reach a younger audience than expected, the far-right party reached an older audience. Researchers hypothesized that algorithmic bias in ad distribution was influenced by known voter behavior, potentially limiting the political participation of certain groups. The lack of transparency in the algorithms used by social media platforms raises questions about the fairness and integrity of political advertising.
The study highlighted the need for greater transparency from social media platforms regarding political advertising to ensure fair and uncompromised elections. The rise of targeted political advertising on social media platforms has sparked concerns among political actors, researchers, and society as a whole. Calls for improved monitoring of electoral advertising to uphold democratic integrity are becoming more prominent. Regulatory efforts, such as the Digital Services Act in the EU, aim to hold social media platforms accountable by providing public access to political and social ads for research purposes.
The study on social media algorithms and political advertising underscores the need for critical examination of the role these algorithms play in shaping political discourse online. The influence of algorithms in promoting certain types of content and parties over others raises important questions about the fairness and transparency of digital political campaigns. Moving forward, efforts to increase transparency and accountability in political advertising on social media platforms are crucial for safeguarding democratic principles and ensuring a level playing field for all political parties.

Leave a Reply