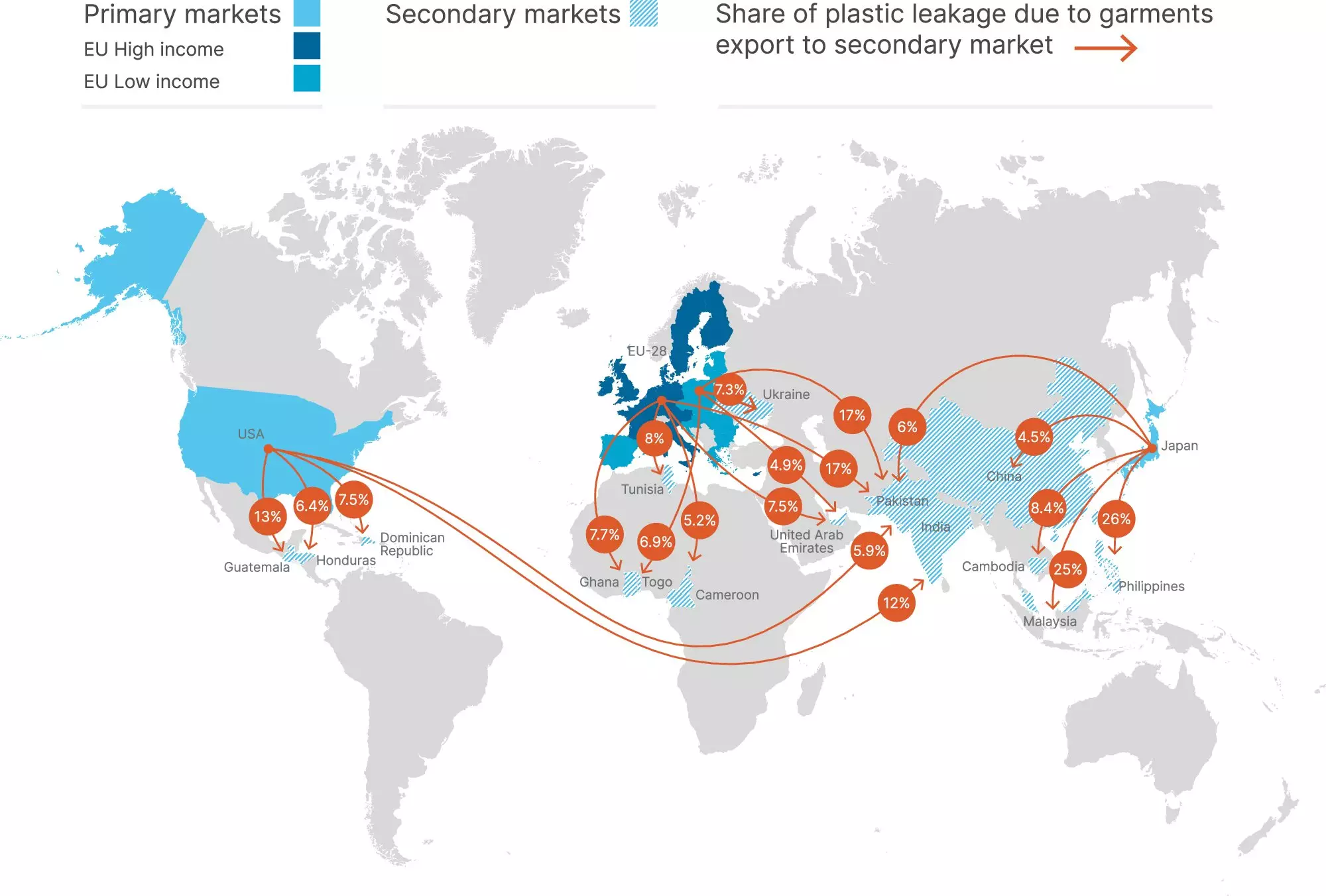
A recent study conducted by researchers at North Carolina State University has brought to light a startling revelation about the global apparel industry. The study found that in 2019 alone, the global apparel industry generated over 20 million tons of plastic waste, with approximately 40% of that waste ending up improperly managed in the environment. This phenomenon, known as “plastic leakage,” is a significant source of pollution that has been largely overlooked until now.
The study divided textile waste into two main categories: clothing made from synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic, and clothing made from natural fibers like cotton. Synthetic apparel was identified as the primary source of plastic waste, accounting for a staggering 89% of all plastic waste generated by the global apparel industry in 2019. In contrast, cotton clothing only contributed 1.9 million tons of plastic waste, mainly from the plastic used in packaging.
One of the key findings of the study was the impact of “fast fashion” culture, particularly in high-income countries like the United States and Japan. The culture of buying a large quantity of clothes and quickly discarding them has led to a significant amount of plastic waste entering the environment. This is exacerbated by the fact that discarded clothes from these countries often end up being sold in lower-income countries with inadequate waste management systems, leading to further pollution.
The study’s conclusion emphasizes the urgent need for significant changes in the global apparel sector to address the plastic leakage issue. A shift towards a more circular framework, where materials are recycled and reused instead of becoming waste, is essential to mitigate the environmental impact of the industry. Additionally, there is a recommendation to increase the use of renewable and non-synthetic textiles to reduce the reliance on plastic-based materials.
The study sheds light on the alarming amount of plastic waste generated by the global apparel industry and the detrimental impact it has on the environment. It serves as a wake-up call for the industry to adopt more sustainable practices and move towards a circular economy model to ensure a healthier planet for future generations.

Leave a Reply