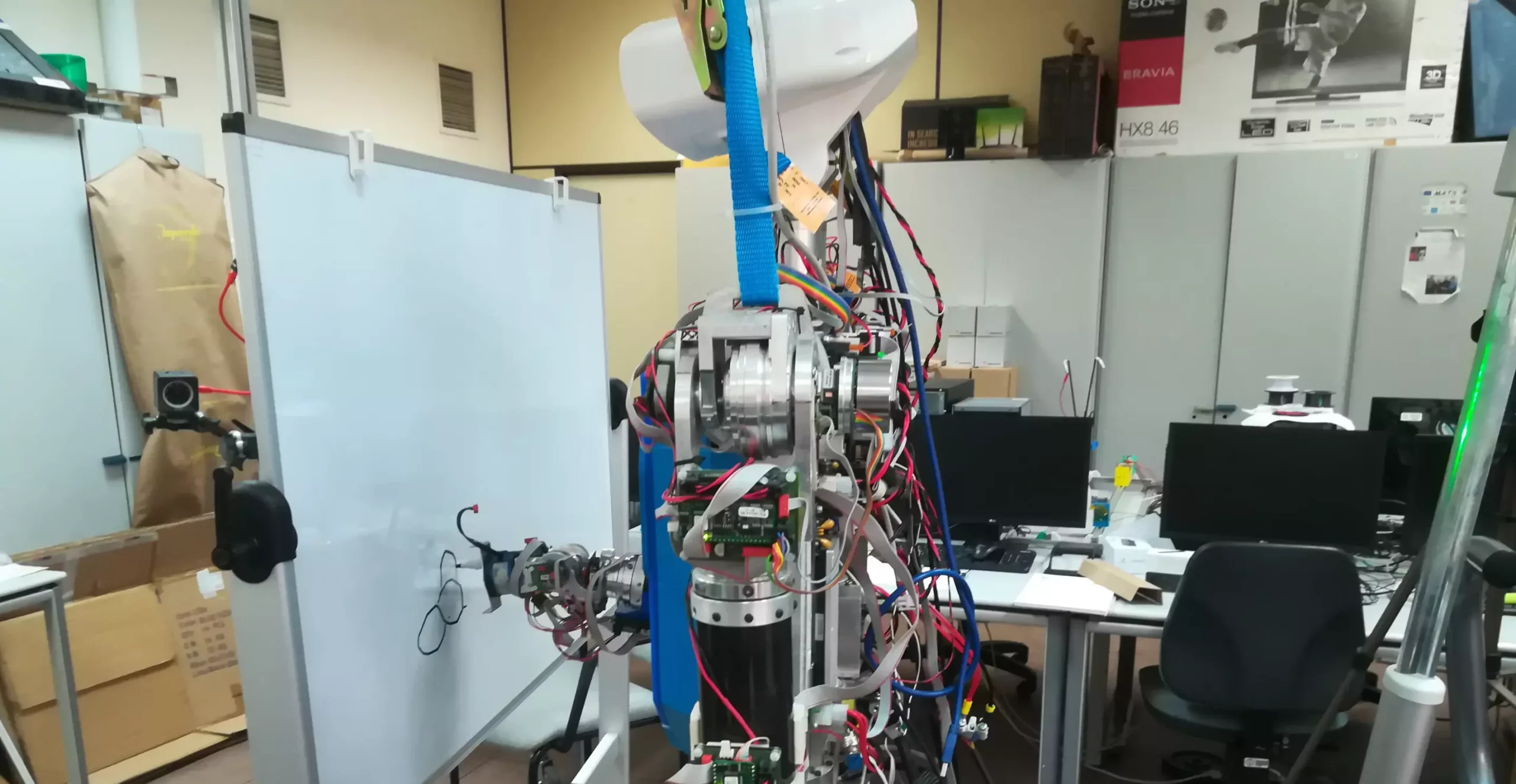
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made significant progress in recent years, particularly in the realm of deep learning algorithms and generative models. These advancements have paved the way for the automated production of striking AI-generated artistic content. While most AI-generated art is typically created by algorithms and computational models, researchers at Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) and Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) have taken a unique approach. Their recent development of a deep learning-based model that enables a humanoid robot to sketch pictures, akin to a human artist, is a groundbreaking example of how robots can actively engage in creative processes.
The team behind this innovative project aimed to create a robot application that would capture the attention of both the scientific community and the general public. According to Raúl Fernandez-Fernandez, co-author of the paper, the idea was to introduce a task that would be visually stunning when performed by a robot. Instead of the traditional approach where robotic systems reproduce images generated by algorithms, the researchers sought to design a robot that could create sketches stroke by stroke, mimicking the process of a human artist. This unique approach required leveraging deep reinforcement learning techniques to enhance the robot’s creative abilities.
Over the past few years, Fernandez-Fernandez and his team have been dedicated to developing sophisticated algorithms to empower creative robots. Their latest paper builds upon previous research efforts, combining promising approaches to refine the robot’s sketching capabilities. Inspired by earlier works that explored the utility of datasets like Quick Draw! and introduced Deep-Q-Learning for complex trajectories, the team devised a robust neural network framework to carefully plan the actions of the robot. This framework comprised three interconnected networks that extracted high-level and low-level features necessary for generating sketches.
The robotic sketching system introduced by the researchers is rooted in a Deep-Q-Learning framework developed in a prior paper by Zhou and colleagues. Fernandez-Fernandez’s team enhanced this framework to effectively guide the robot’s actions, enabling it to perform intricate manual tasks across diverse environments. By dividing the neural network into distinct parts and feeding it with relevant input channels like distance-related and painting tool information, the researchers optimized the network’s training process, enhancing its sketching accuracy.
One of the key challenges the researchers faced was translating AI-generated images into physical sketches on a canvas. To address this, they created a virtual space within the physical canvas, enabling the robot to move and translate the painting positions as directed by the model. This innovative control strategy not only facilitated the robot’s creation of art but also showcased the potential for advanced control algorithms within real-world applications. Fernandez-Fernandez emphasized that the introduction of such algorithms could pave the way for original and high-level robot applications beyond conventional problem-solving approaches.
Read More: The Future of Private Space Exploration: A Texas Company’s Mission to the Moon
The recent breakthrough by Fernandez-Fernandez and his team represents a significant step towards integrating robots into the realm of artistry. By imbuing robots with human-like painting skills and leveraging deep learning techniques, the researchers hope to inspire future studies that explore the intersection of AI and creativity. Their use of Deep Q-Learning to extract human emotions and transfer them to robots opens up new possibilities for emotive robotic interactions. Moving forward, these advancements may contribute to the development of control policies that enable robots to tackle complex tasks with finesse, ushering in a new era of artistic robotics.
Overall, the work by Fernandez-Fernandez and his collaborators underscores the transformative potential of integrating advanced AI algorithms with robotic systems. By blurring the lines between human creativity and machine intelligence, these researchers are not only pushing the boundaries of AI-generated art but also redefining the role of robots in the creative process. As we look towards the future, the prospect of robots becoming artists in their own right seems increasingly plausible, heralding a new chapter in the evolution of art and technology.

Leave a Reply