In our modern age of data-driven decision-making, efficiency in solving complex problems is paramount. However, the limitations of traditional computers, such as the von Neumann bottleneck, have hindered their ability to effectively tackle problems with numerous interacting variables. To overcome this challenge, a new approach known as collective state computing has emerged, drawing inspiration from the Ising problem in magnetism to optimize problem-solving processes.
Collective state computing involves representing a problem as a graph, where nodes are interconnected by edges. Each node is assigned one of two states, either +1 or -1, which symbolize potential solutions to the problem at hand. The objective is to identify the configuration that minimizes the total energy of the system, as defined by a Hamiltonian. This approach enables researchers to explore physical systems that may outperform traditional computers in efficiently solving complex optimization problems.
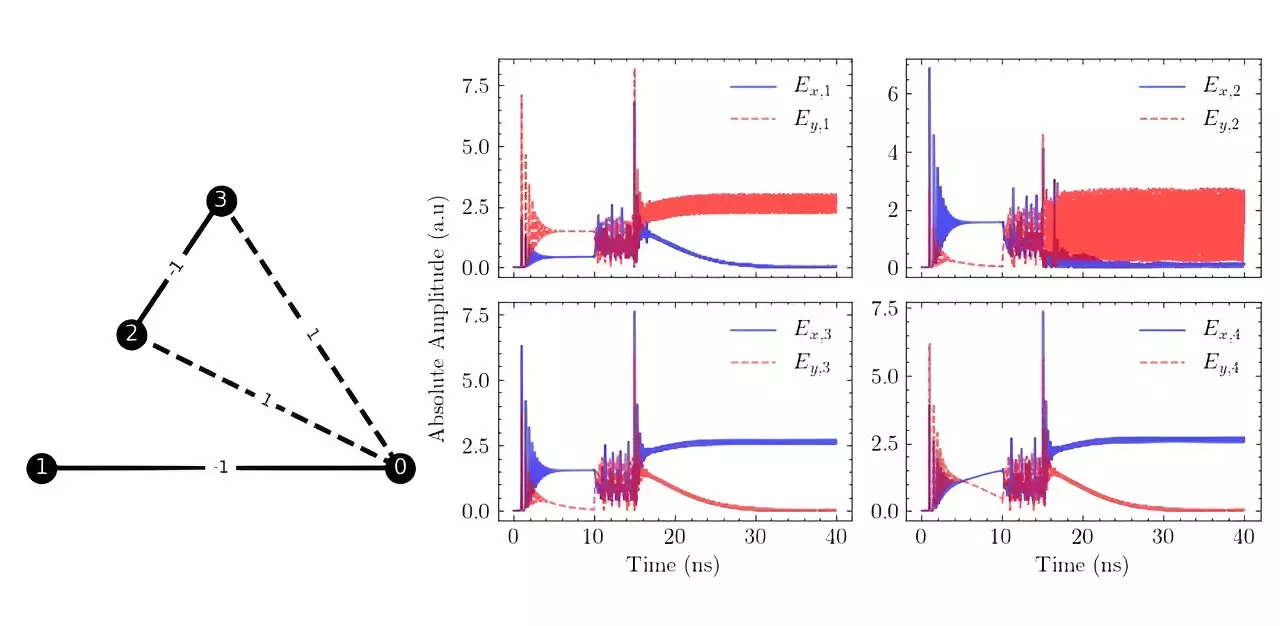
One innovative method being explored in the realm of collective state computing involves leveraging light-based techniques. By encoding information into properties like polarization state, phase, or amplitude, these systems can rapidly identify the optimal solution by capitalizing on phenomena such as interference and optical feedback. A recent study conducted by researchers from the National University of Singapore and the Agency for Science, Technology, and Research delved into the use of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) to tackle Ising problems.
Read More: A New Outbreak of Alaskapox Raises Concerns
The researchers tested their VCSEL-based system on 2-, 3-, and 4-bit Ising problems, yielding encouraging outcomes. However, they also encountered obstacles, including the prerequisite for minimal VCSEL lasing anisotropy, which presents a potential hurdle in practical implementation. Nevertheless, successfully overcoming these challenges could pave the way for the development of an all-optical VCSEL-based computer architecture capable of solving problems that are currently beyond the reach of conventional computers.
Collective state computing represents a groundbreaking approach to optimizing problem-solving processes in the era of big data. By harnessing innovative technologies such as VCSELs and exploring the fascinating principles of the Ising problem, researchers are pushing the boundaries of traditional computing paradigms. The journey towards realizing an all-optical computing architecture is fraught with challenges, but the potential rewards in terms of efficiency and problem-solving capabilities are limitless.

Leave a Reply