In a ground-breaking study led by Prof. Meital Reches of the Hebrew University, alongside Ph.D. student Mr. Daniel Boas and a team of collaborators, a new drug delivery system has been introduced. This system revolves around switchable peptide-stabilized emulsions, marking a significant advancement in the field of drug delivery. This innovative approach is poised to revolutionize drug transport by enabling the simultaneous carriage of both water-soluble and water-insoluble compounds within a single carrier, addressing previous constraints associated with traditional methods.
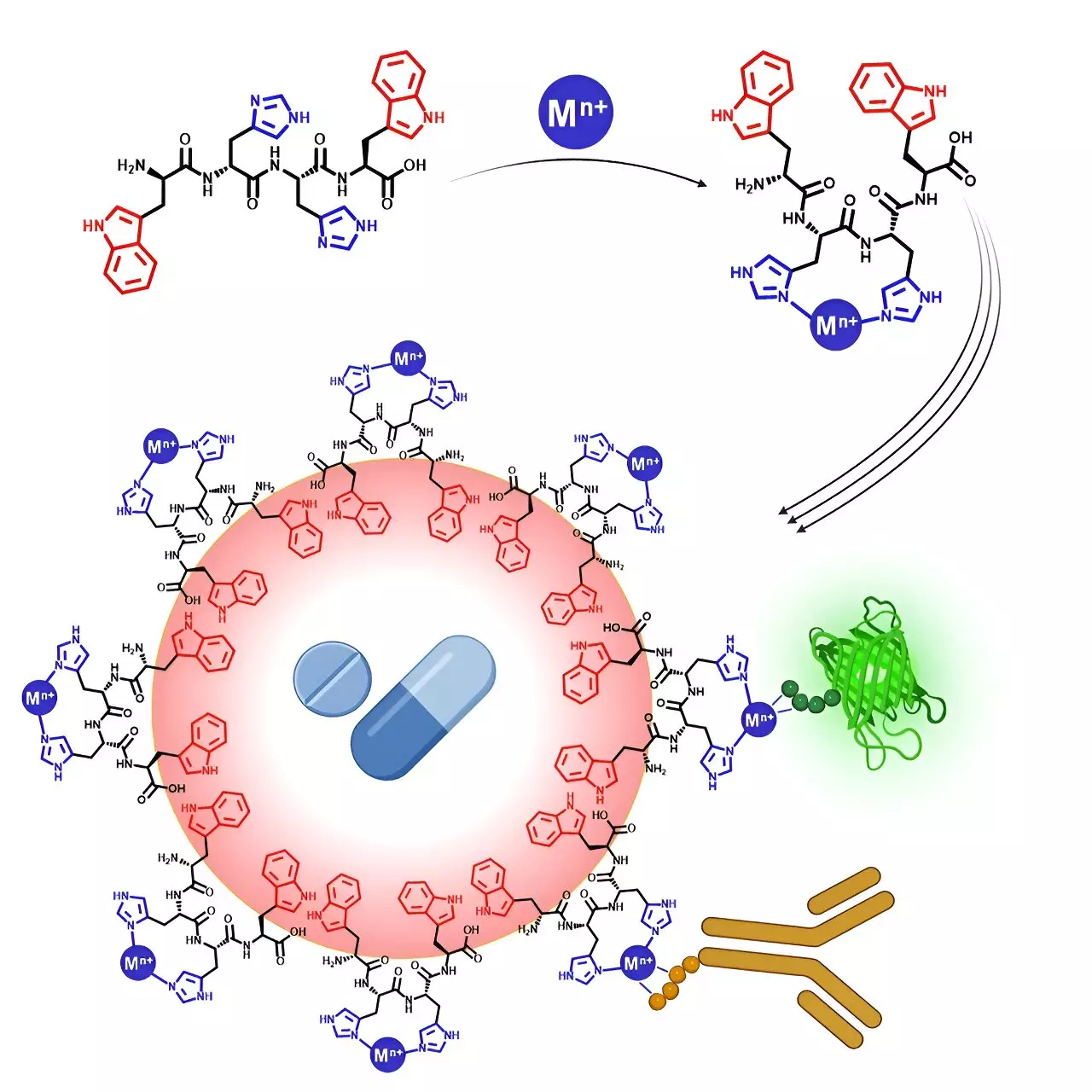
Traditionally, emulsions have been utilized as reliable carriers for drug delivery; however, their effectiveness has been limited by the inability to encapsulate both types of drugs in a single vehicle. To overcome this challenge, Prof. Reches’ team developed a short peptide composed of only four amino acids. This peptide possesses the unique ability to stabilize emulsions and accommodate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds. The key to this innovation lies in the peptide’s capability to change its shape upon binding specific metal ions, transitioning from hydrophilic to amphiphilic. This metamorphosis at the molecular level not only stabilizes emulsions containing water-insoluble drugs but also facilitates the transportation of water-soluble metal ions linked to the peptide.
The peptide’s adaptability to bind with various metal ions enables it to adhere to both water and fat, thereby maintaining the stability of the drug blend. Moreover, it can transport metal ions that dissolve in water, showcasing a versatile drug delivery system with multifaceted capabilities. To comprehend the intricacies of these emulsions, researchers employed advanced techniques such as spectroscopy, NMR, and molecular dynamics. Their analyses unveiled that the stability of these emulsions originates from bonds between histidine and metal, which can be reversed under low pH conditions commonly encountered in tumor cells. This unique feature ensures the precise release of drugs at specific sites, enhancing treatment efficacy.
Potential Impact and Future Prospects
Initial trials utilizing paclitaxel-loaded emulsions have displayed promising outcomes, indicating substantial efficacy against cancer cells. Beyond drug delivery, this adaptable system offers a range of possibilities for customization, paving the way for innovative applications and enhanced benefits in various fields. The future of drug delivery seems brighter with the advent of peptide-stabilized emulsions, offering a glimpse into a new era of efficient and targeted drug administration.

Leave a Reply