In a groundbreaking study by the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) in Japan, researchers have developed a novel approach to the reduction of esters using light as an energy source. Traditionally, the process of ester reduction has been costly and harmful to the environment, requiring excess amounts of highly reactive metal reductants. However, with the use of sustainable photocatalysts, this process can now be achieved in a more sustainable and efficient manner.
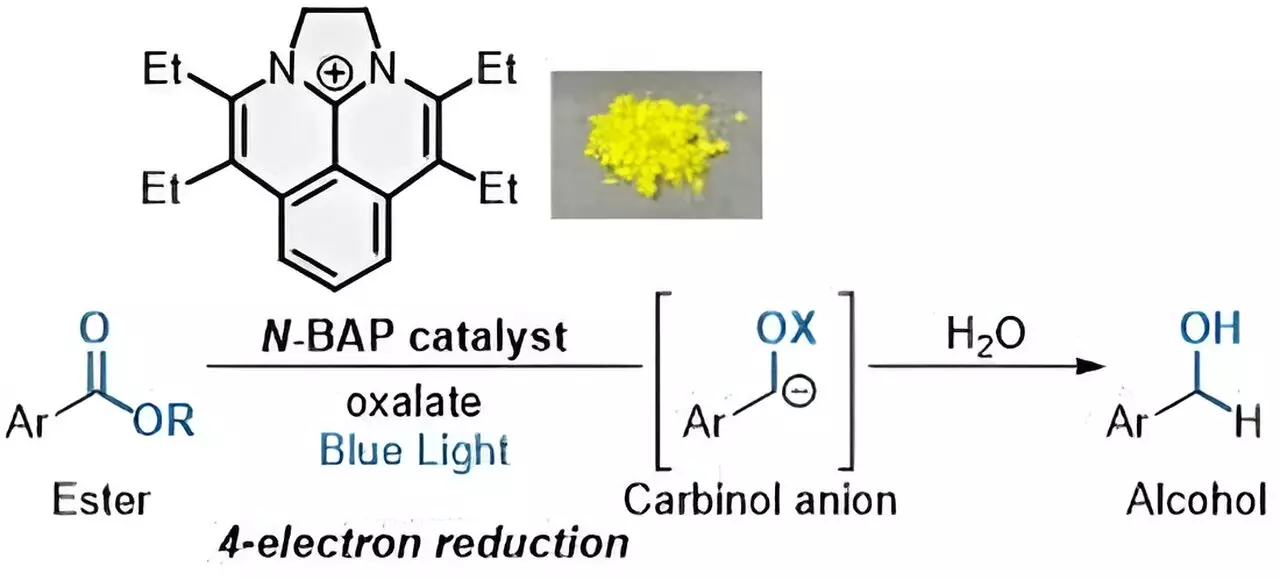
In the past, ester reduction involved adding electrons to the compound, forcing the ester to reduce to its more basic components. This process typically required the use of expensive and non-renewable noble metals, resulting in limited reduction of organic compounds. However, with the development of new photocatalysts like “N-BAP,” researchers have been able to achieve a quadruple electron transfer process, leading to the production of desired alcohols.
Achieving Sustainable Development Goals
As the world moves towards achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the importance of sustainable practices in organic synthesis becomes increasingly crucial. Photocatalytic reactions using visible light as an energy source have emerged as a desirable method for achieving these goals. By utilizing photocatalysts in the reduction of esters, researchers are able to promote redox reactions without the need for highly reactive metal reductants, thus reducing the environmental impact of the process.
The development of the N-BAP photocatalyst has revolutionized the process of ester reduction. When irradiated with blue light, the N-BAP catalyst initiates a reaction that adds four electrons to the ester in quick succession, resulting in the formation of alcohols. By combining the N-BAP catalyst with oxalate as a traceless reductant, researchers have been able to achieve a rapid and efficient four-electron reduction of esters, paving the way for a more sustainable approach to ester reduction.
The use of photocatalysts in ester reduction represents a significant advancement in the field of organic synthesis. By harnessing the power of light as an energy source, researchers are able to achieve the reduction of esters in a more sustainable and efficient manner. With further development and research in this area, the future of ester reduction looks promising, offering a pathway towards achieving the goals of sustainable development.

Leave a Reply