Implantable medical devices have long relied on traditional batteries to function, leading to the need for frequent invasive surgeries for replacement. However, researchers in China have introduced a groundbreaking concept – an implantable battery that runs on oxygen within the body. This innovative approach could potentially transform the field of medical technology, eliminating the limitations of conventional batteries.
The study, recently published in the journal Chem, demonstrates the feasibility of utilizing oxygen as a continuous power source for implantable devices. Corresponding author Xizheng Liu highlights the significance of oxygen as the source of life and emphasizes how leveraging this abundant resource in the body can extend the battery life indefinitely. By tapping into the body’s natural oxygen supply, the need for battery replacements may become a thing of the past.
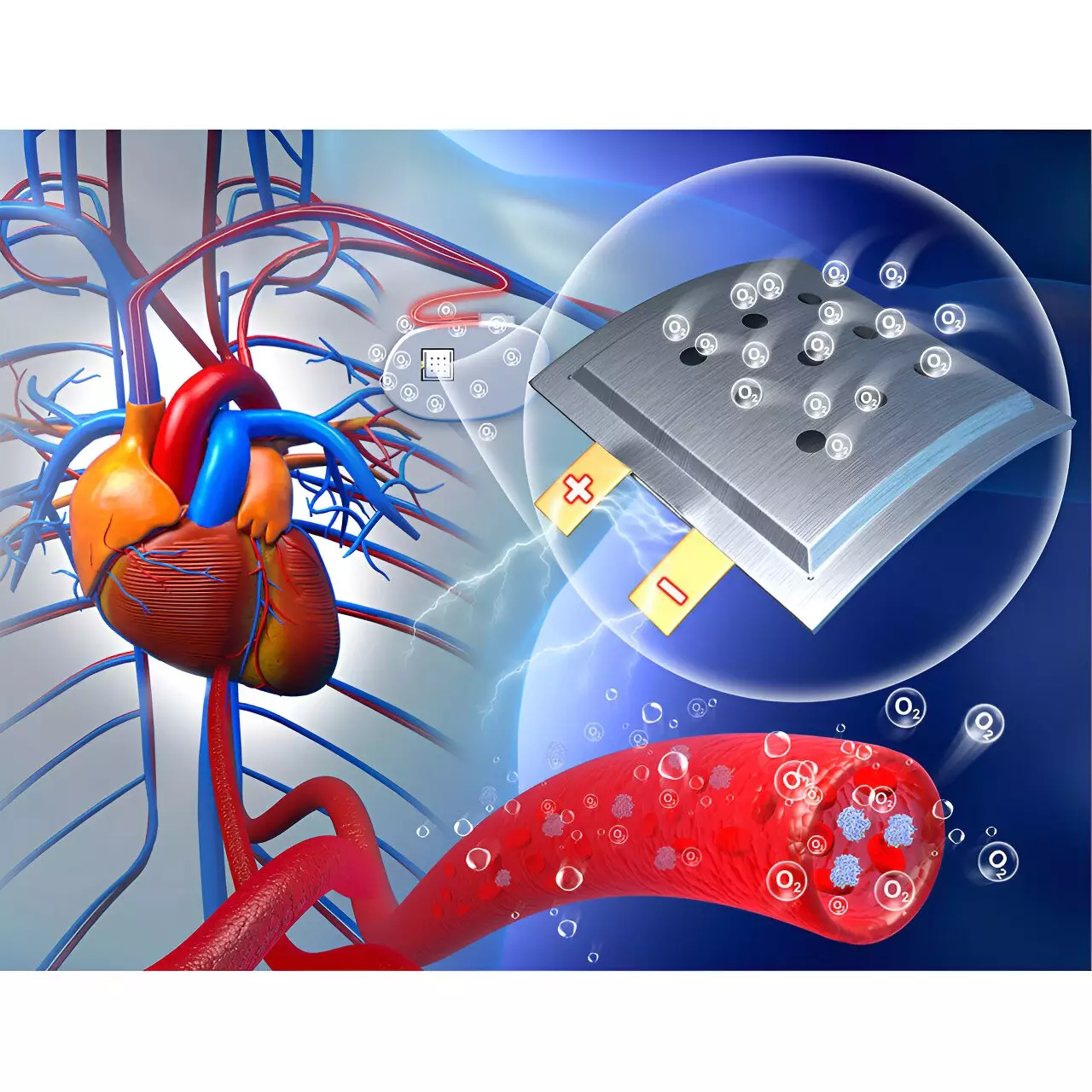
Design and Functionality of the Oxygen-Powered Battery
To create a safe and efficient battery system, the researchers utilized electrodes made of a sodium-based alloy and nanoporous gold. These materials interact with oxygen in the body to generate electricity, providing a stable power source for implantable devices. The battery is encapsulated in a soft and flexible polymer film to ensure biocompatibility and protection. In animal studies involving rats, the battery demonstrated consistent voltage output and a power density of 2.6 µW/cm2.
One of the key findings of the study was the favorable response of the body to the implanted battery. The rats exhibited no signs of inflammation, and metabolic processes effectively cleared byproducts of the battery’s chemical reactions. Remarkably, the presence of the battery stimulated tissue regeneration, including the regrowth of blood vessels around the implant site. This unexpected outcome suggests potential applications in monitoring wound healing processes.
Future Directions and Potential Applications
Looking ahead, the research team plans to enhance the battery’s energy output by exploring alternative electrode materials and optimizing the battery design. The scalability of production and the use of cost-effective materials could further drive down the cost of these innovative devices. Beyond powering medical implants, the oxygen-powered battery may have implications in the field of oncology. By starving tumor cells of oxygen or converting energy into heat to target cancer cells, this technology shows promise in cancer treatment.
The development of an oxygen-powered battery for implantable medical devices represents a significant advancement in the field of biomedical engineering. By harnessing the body’s own resources, researchers are paving the way for more sustainable and efficient medical technologies. With continued research and innovation, the future of implantable devices looks brighter than ever.

Leave a Reply