Traditional two-terminal devices have long been the norm in electronic components, but they often come with limitations that can hinder a system’s performance. However, a recent development by researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China has introduced a new three-terminal diode that not only emits light but also detects it. This breakthrough could revolutionize wireless communication and light-driven computing systems by significantly enhancing their capabilities.
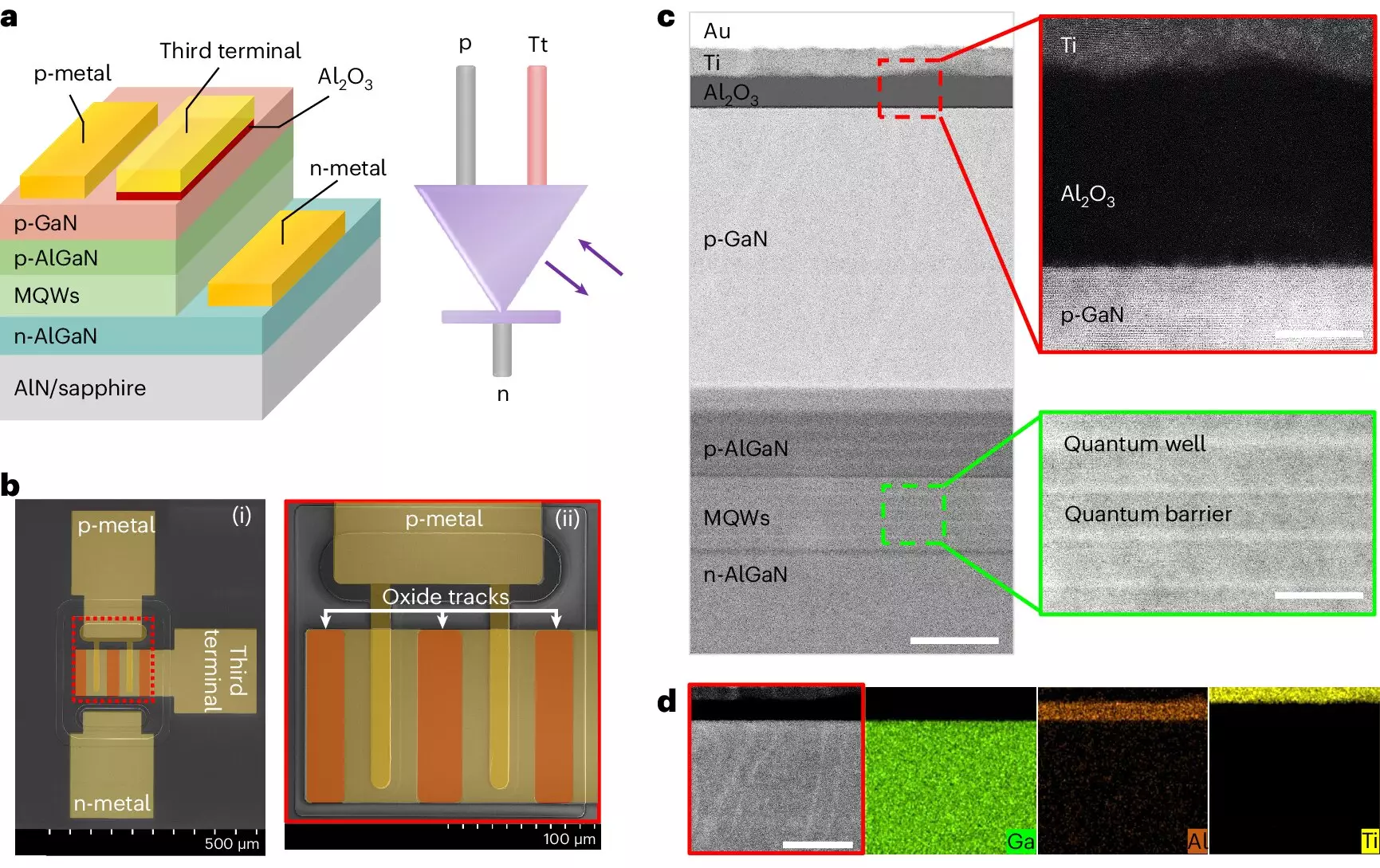
The innovative three-terminal diode combines a traditional gallium nitride-based p–n diode with a newly introduced third terminal made up of a metal/Al2O3 dielectric layer directly applied to the p–GaN layer. This new design allows the device to function as both a light emitter and a photodetector, giving it a versatility that was previously unattainable with two-terminal devices.
Initial tests of the three-terminal diode have shown that it can enhance modulation bandwidth by more than 64% compared to current OWC systems that use classic light-emitting p–n diodes. This improvement opens up new possibilities for faster and more efficient data transmission methods, making it a promising technology for the future of OWC systems.
The potential applications of the new three-terminal diode are vast, ranging from high-speed data transmission in OWC technology to the development of optically driven computing systems. The researchers behind this breakthrough are already looking ahead, with plans to further enhance the performance of their diode and explore integration with other optoelectronic materials and systems. This ongoing research is paving the way for the development of multifunctional and integrated electronic and optoelectronic systems that could shape the future of technology.
The development of the three-terminal diode represents a significant advancement in the field of optoelectronics. By overcoming the limitations of traditional two-terminal devices, this new diode opens up new avenues for innovation and improvement in wireless communication and computing systems. As researchers continue to explore the possibilities of this technology, we can expect to see even more exciting developments on the horizon.

Leave a Reply