In a recent study published in Geophysical Research Letters, researchers delved into the intricate relationship between elevation and climate heterogeneity. This study, led by Yanlong Guan from Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University in China, aimed to understand how changes in elevation can influence organismal diversity across different climate zones. By analyzing data from over 4,000 weather stations worldwide spanning a 70-year period, the researchers were able to identify distinct patterns in climate variability.
Effects of Elevation on Climate Heterogeneity
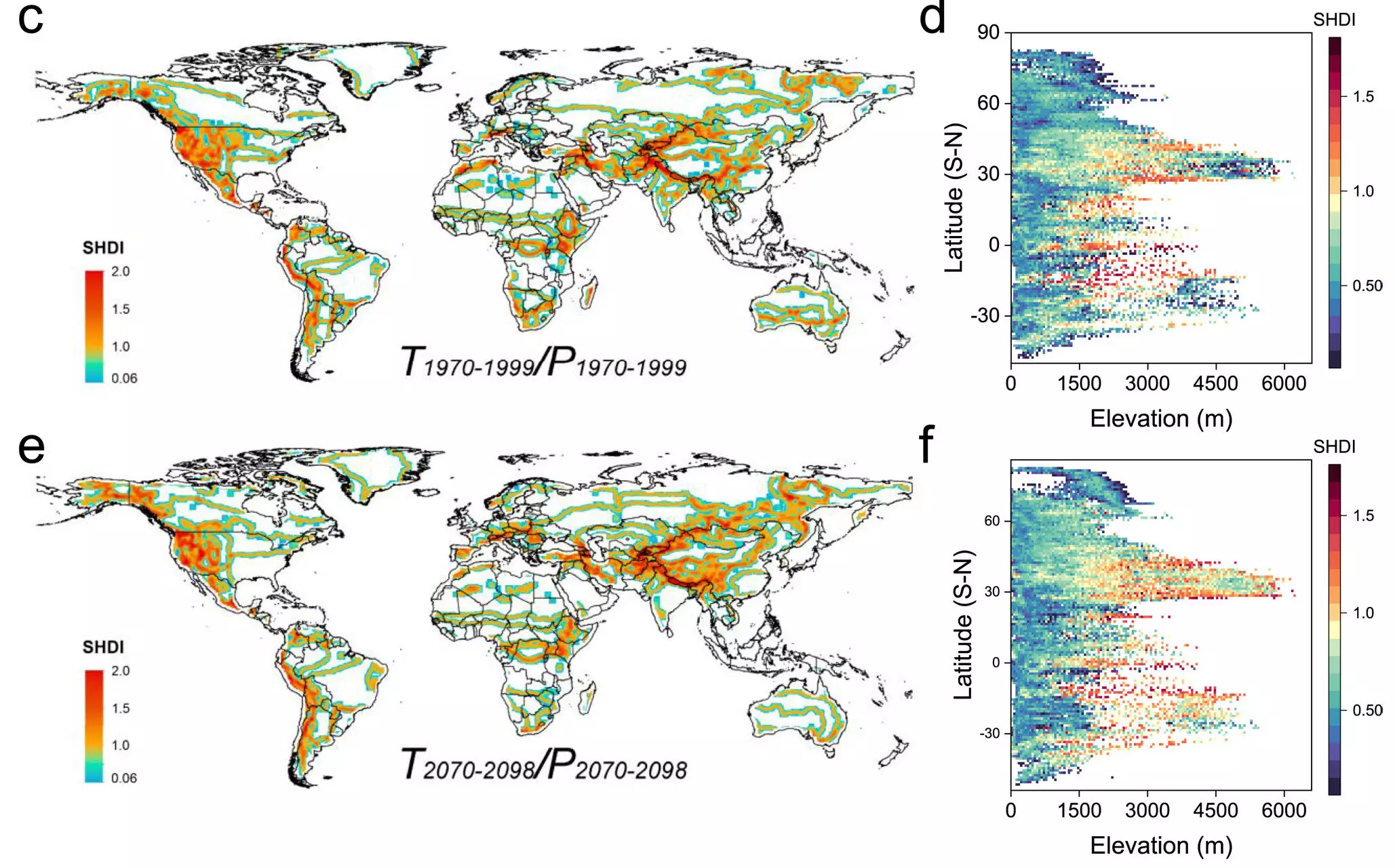
One of the key findings of the study was the impact of elevation on climate heterogeneity. The researchers observed that at lower elevations (less than 2,000 m), there was a reduction in Shannon’s diversity index. This decrease in organismal diversity was attributed to the higher and faster rise in temperatures at lower altitudes, leading to the proliferation of similar arid and tropical conditions over a wide area. In contrast, higher elevations (above 2,000 m) displayed greater climate heterogeneity, with the diversity index continuing to increase in these areas. This suggests that higher altitudes experience slower warming trends, allowing for a more diverse range of climatic conditions to persist.
The researchers also used climate simulations to explore the driving forces behind these patterns in climate heterogeneity. Unsurprisingly, anthropogenic climate change emerged as a significant factor influencing the shift in climate variability between lower and higher altitudes. The simulations projected that by the end of the century, up to 46% of land surfaces could transition to warmer and drier conditions, posing a threat to habitat and species distributions. This homogenization of climate types highlights the importance of understanding the persistent climate variability at higher elevations, which may serve as refugia for human, animal, and plant communities seeking more favorable conditions amidst rising temperatures.
As the planet continues to warm, the role of elevation in shaping climate patterns becomes increasingly crucial. Identifying regions that exhibit strong climate heterogeneity, such as high-altitude refugia, will be essential for conservation efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity in the face of climate change. By understanding the complex interplay between elevation, temperature, and precipitation, researchers and policymakers can better anticipate and mitigate the impacts of climate change on global ecosystems. The findings from this study underscore the importance of preserving diverse climatic conditions to safeguard the resilience of Earth’s ecosystems in the decades to come.

Leave a Reply