A recent study conducted by a group of physicists and oceanologists from Germany has shed light on the potential consequences of rising global temperatures on extreme El Niño events. This research, published in Geophysical Research Letters, utilized the CESM1 climate model to explore the possibility of a tipping point being reached in the coming decades if current emissions continue unabated.
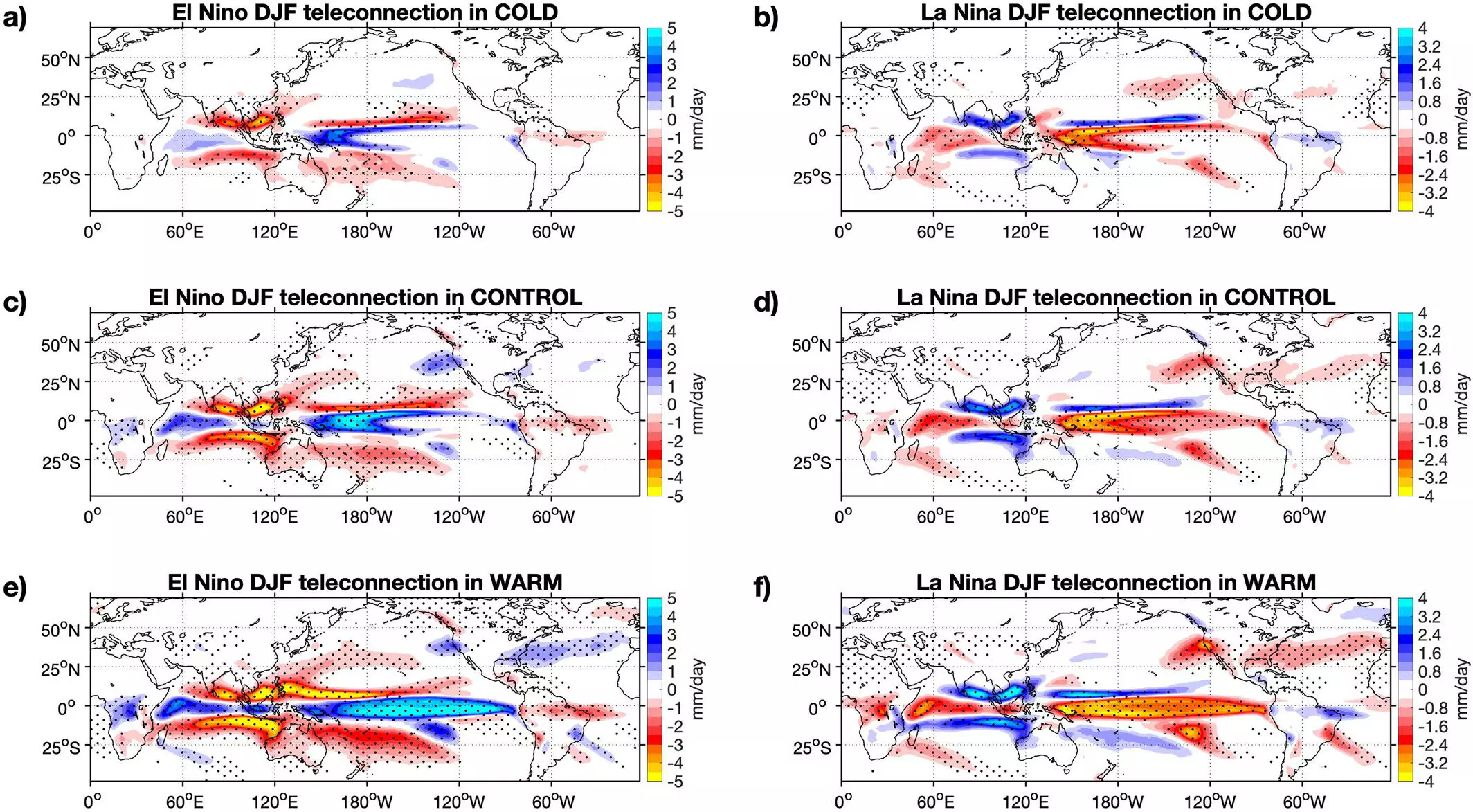
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a crucial climate phenomenon that plays a significant role in shaping weather patterns around the globe. Heat release from certain parts of the ocean can lead to increased rainfall in some regions while causing droughts in others. Over the years, observations have indicated a trend towards more extreme ENSO events, sparking concerns about the frequency and intensity of such occurrences.
The researchers behind this study delved into historical data and incorporated information from previous studies to create simulations under varying temperature scenarios. The results of their work revealed alarming projections – a potential increase of 2.9°C by 2100 and a tipping point at 3.7°C, where almost all ENSO events could be deemed extreme. This suggests a future where extreme weather events become the norm, with profound implications for various regions across the globe.
If these projections come to fruition, the ramifications could be devastating. The researchers noted that even if measures were taken to halt climate change, the effects would persist for centuries, indicating a long-lasting impact on weather patterns. Furthermore, the model predicted more frequent extreme ENSO events, occurring as frequently as every four years, leading to significant disruptions in precipitation patterns and potentially catastrophic outcomes for affected regions.
The study underscores the urgency of addressing climate change and curbing greenhouse gas emissions to prevent a future where extreme weather events become the new normal. The findings serve as a stark warning of the potential consequences of unchecked global warming on El Niño events and highlight the critical need for immediate action to mitigate these threats.

Leave a Reply