As wildfires in Siberia continue to increase in frequency, researchers are warning of significant global impacts on climate, air quality, health, and economies in East Asia and across the northern hemisphere. Recent studies have shown that the effects of escalating wildfires in Siberia could have far-reaching consequences that go beyond just the immediate region.
A team of researchers from Hokkaido University, the University of Tokyo, and Kyushu University conducted global numerical simulation experiments to assess the potential impacts of intensifying wildfires in Siberia. Their findings, published in the journal Earth’s Future, indicate that under the most extreme wildfire scenarios, there could be substantial and widespread effects on various aspects of the environment and economy.
Atmospheric Aerosols and Climate
One of the primary ways in which wildfires affect the atmosphere is through the emission of atmospheric aerosols. These tiny particles suspended in the air can have significant implications for air quality and climate. The researchers utilized a Japanese global climate modeling system to analyze the impact of Siberian wildfires on atmospheric aerosols and their subsequent effects on the environment.
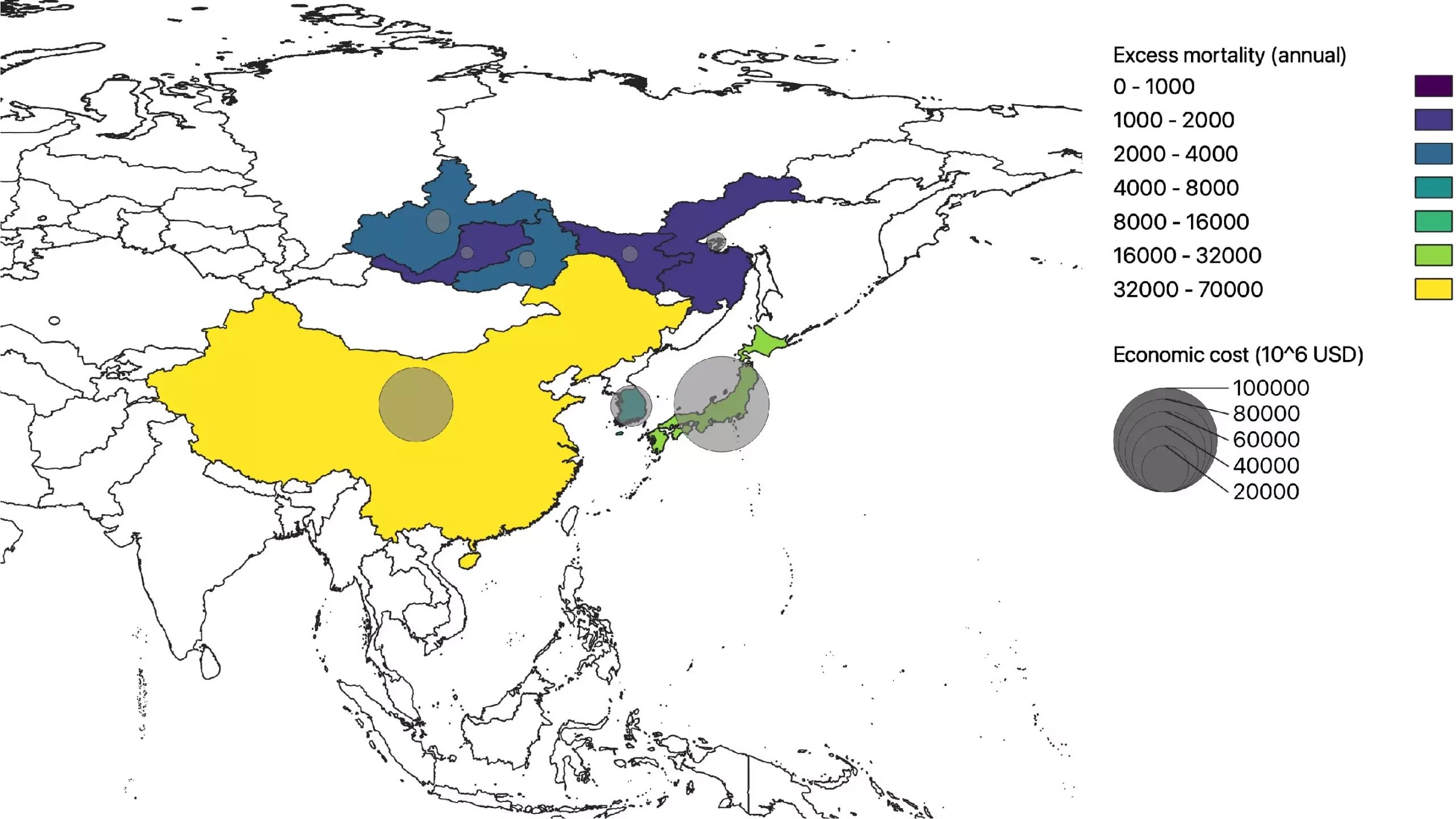
The modeling results suggest that the increased intensity of wildfires in Siberia could lead to a cooling effect across the northern hemisphere, potentially mitigating some of the warming associated with global climate change. However, this cooling effect is also likely to result in worsened air quality in regions downwind of the wildfires. This could have serious implications for public health, with increased instances of respiratory illnesses and premature mortality expected.
In addition to health concerns, the economic impacts of escalating wildfires in Siberia are also a cause for alarm. The study estimates that the direct impact of increased deaths due to air pollution could lead to health-related costs amounting to billions of US dollars annually. However, the true economic toll could be even greater when accounting for non-fatal illnesses, absenteeism from work, and reduced educational opportunities.
Associate Professor Teppei Yasunari emphasizes the urgent need for increased efforts to address the effects of Siberian wildfires to prevent excess deaths, illnesses, and economic losses. The modeling results underscore the importance of taking proactive measures to mitigate the impacts of wildfires in the region.
The far-reaching effects of wildfires in Siberia highlight the need for a better understanding of their impact on climate, air quality, and economies. As global warming continues to exacerbate the frequency and intensity of wildfires, it is crucial to develop strategies to limit their effects and protect the environment and public health. The findings of this study serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need to address the growing threat of wildfires in Siberia and their implications for the broader global community.

Leave a Reply