Current building design methods are constantly evolving to address the risks associated with structural failures. Traditional approaches focus on enhancing the connectivity between components within a structure to ensure load redistribution in the event of component failure. While effective in some scenarios, these methods may inadvertently increase the potential for progressive collapse after significant initial failures, as seen in recent building collapses such as the Champlain Towers, Peñíscola incident in 2021, and the collapse in the Iranian city of Abadan in 2022.
A new design method, originating from ICITECH-UPV (Universitat Politècnica de València), offers a groundbreaking solution to mitigate the risk of progressive collapse in buildings. Published in the journal Nature, this innovative approach introduces the concept of fuse-based segmentation, aimed at isolating damaged portions of a structure to prevent the spread of catastrophic failures throughout the entire building.
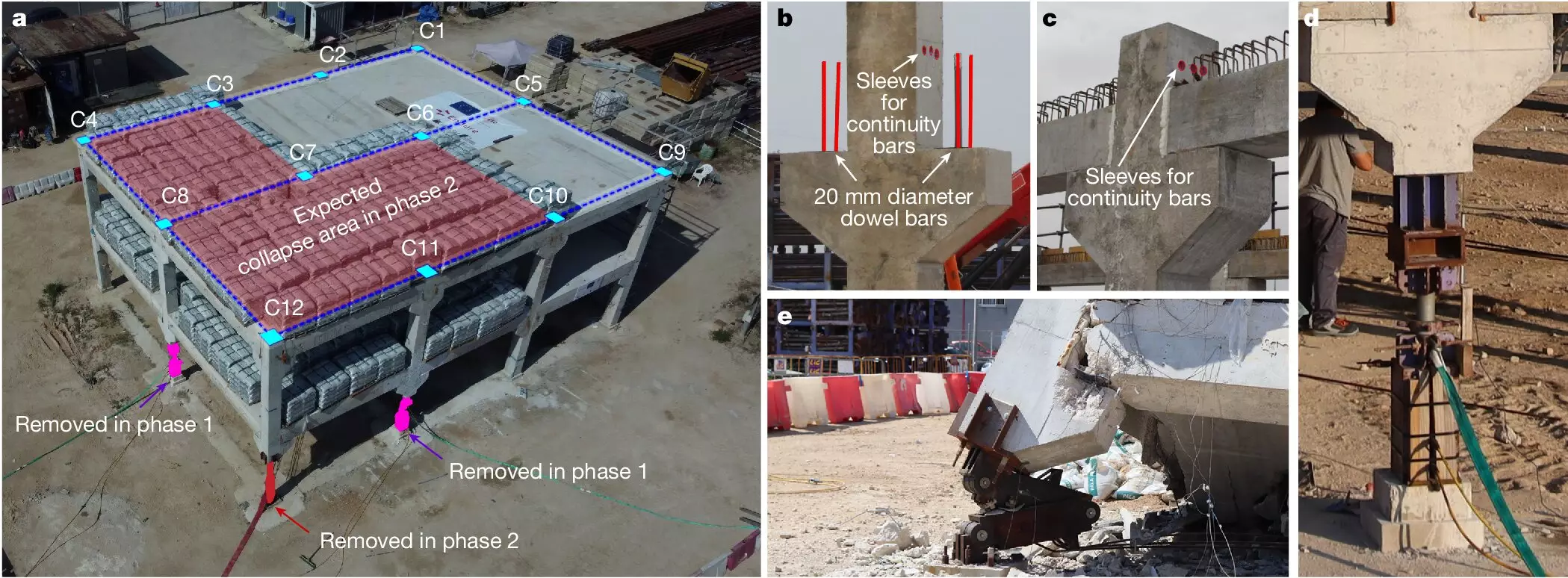
The core principle of the ICITECH-UPV team’s method revolves around the use of a structural fuse, akin to safeguarding an electrical system against overloads by employing electrical fuses. With this approach, the building maintains structural continuity under normal conditions but automatically segments vulnerable areas when failure propagation becomes unavoidable. According to Nirvan Makoond, “The new design philosophy significantly reduces the extent of damages and averts total collapse.”
An essential aspect of the fuse-based segmentation method is its cost-effectiveness in building construction. By utilizing conventional construction materials and techniques, the implementation of this approach is projected to have minimal to negligible impacts on the overall structural cost. Andri Setiawan notes, “The method remains economically viable while enhancing building resilience.”
The validation of the new design method through full-scale building tests marks a significant milestone in building safety and resilience. As Jose M. Adam emphasizes, “The successful test results confirm the effectiveness of the approach in preventing catastrophic collapses and safeguarding human lives.” The current focus of the researchers is to extend the methodology to buildings constructed with different materials, such as in-situ concrete and steel.
The development of the fuse-based segmentation method showcases one of the most prominent outcomes of the Endure project. Through a world-first full-scale building test conducted in June 2023, the performance of the approach was successfully validated, demonstrating its capability to confine large initial failures within isolated building sections. Notably, all research activities related to this innovative design method were exclusively conducted at the UPV, underscoring the academic excellence of the institution and its research team.
The implementation of fuse-based segmentation in building design represents a transformative leap forward in enhancing structural resilience and preventing catastrophic collapses. With its proven effectiveness and cost-effective nature, this innovative approach promises to revolutionize the construction industry’s approach to building safety and durability.

Leave a Reply