Chemists at the University of Münster have made groundbreaking advancements in the selective integration of the difluoromethyl group into pyridines, a vital development in drug research and development. This method has the potential to revolutionize the synthesis of bioactive molecules, ultimately leading to the creation of new drugs and agrochemicals.
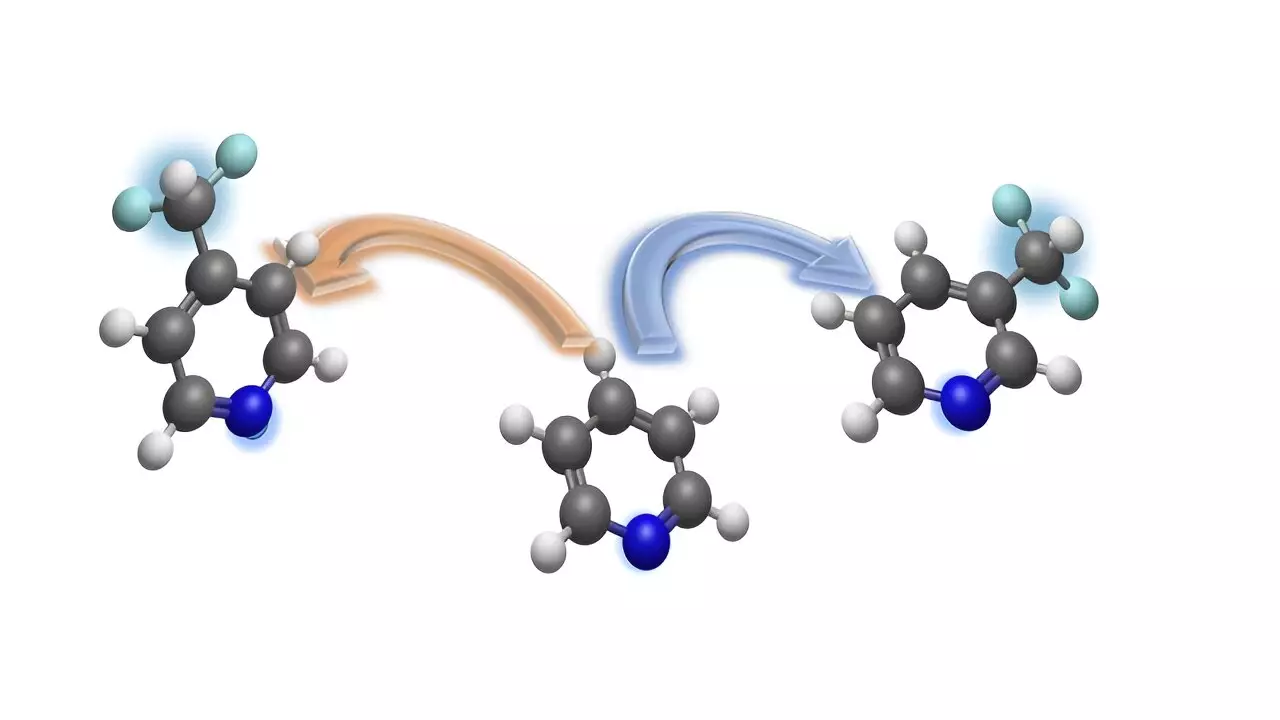
The difluoromethyl group, composed of carbon, two fluorine atoms, and a hydrogen atom, is a critical component in determining the properties of bioactive molecules. By strategically replacing hydrogen atoms in pyridines with difluoromethyl groups, chemists can create novel ring structures that have the potential to become important drug candidates.
Led by Prof Dr. Armido Studer, a team of researchers at the University of Münster has devised a new strategy for precisely introducing the difluoromethyl group into pyridines at specific sites. This innovative approach has been documented in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, marking a significant milestone in the field of organic chemistry.
Pyridines are essential building blocks in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries due to their role in producing biologically active substances. With the new method developed by the research team, chemists can introduce the difluoromethyl group at either the meta-position or the para-position of pyridines, a process that was previously regarded as a challenge in the field.
The method developed by the team at the University of Münster is not only innovative but also practical and cost-effective. By utilizing commercially available reagents, chemists can easily carry out the difluoromethylation process without the need for complex and expensive materials. This accessibility has the potential to revolutionize drug design and streamline the synthesis process.
The integration of the difluoromethyl group into pyridines represents a significant advancement in the field of organic chemistry. This breakthrough has the potential to lead to the development of new drugs and agrochemicals that could have a profound impact on the pharmaceutical industry. The research conducted by the team at the University of Münster showcases the power of innovation and collaboration in advancing scientific knowledge and technological capabilities.

Leave a Reply