The realms of optical illusions, quantum mechanics, and neural networks may seem disparate at first glance. However, a recent study published in APL Machine Learning has delved into the fusion of these seemingly unrelated fields. The research explores the utilization of “quantum tunneling” to develop a neural network capable of perceiving optical illusions akin to human cognition. By examining renowned illusions like the Necker cube and Rubin’s vase, this study has unveiled the potential of quantum-inspired neural networks in vision-based tasks.
Unraveling Optical Illusions
Optical illusions possess the uncanny ability to deceive our visual perception, presenting images that may not align with reality. While the mechanisms behind optical illusions remain elusive, studying them offers insights into the complexities of human cognition and the failures it may entail, such as in conditions like dementia or during extended space journeys. When it comes to AI systems mimicking human vision, optical illusions present a significant challenge. Despite advancements in computer vision, many systems struggle with deciphering optical illusions, highlighting the need for innovative approaches like those explored in this research.
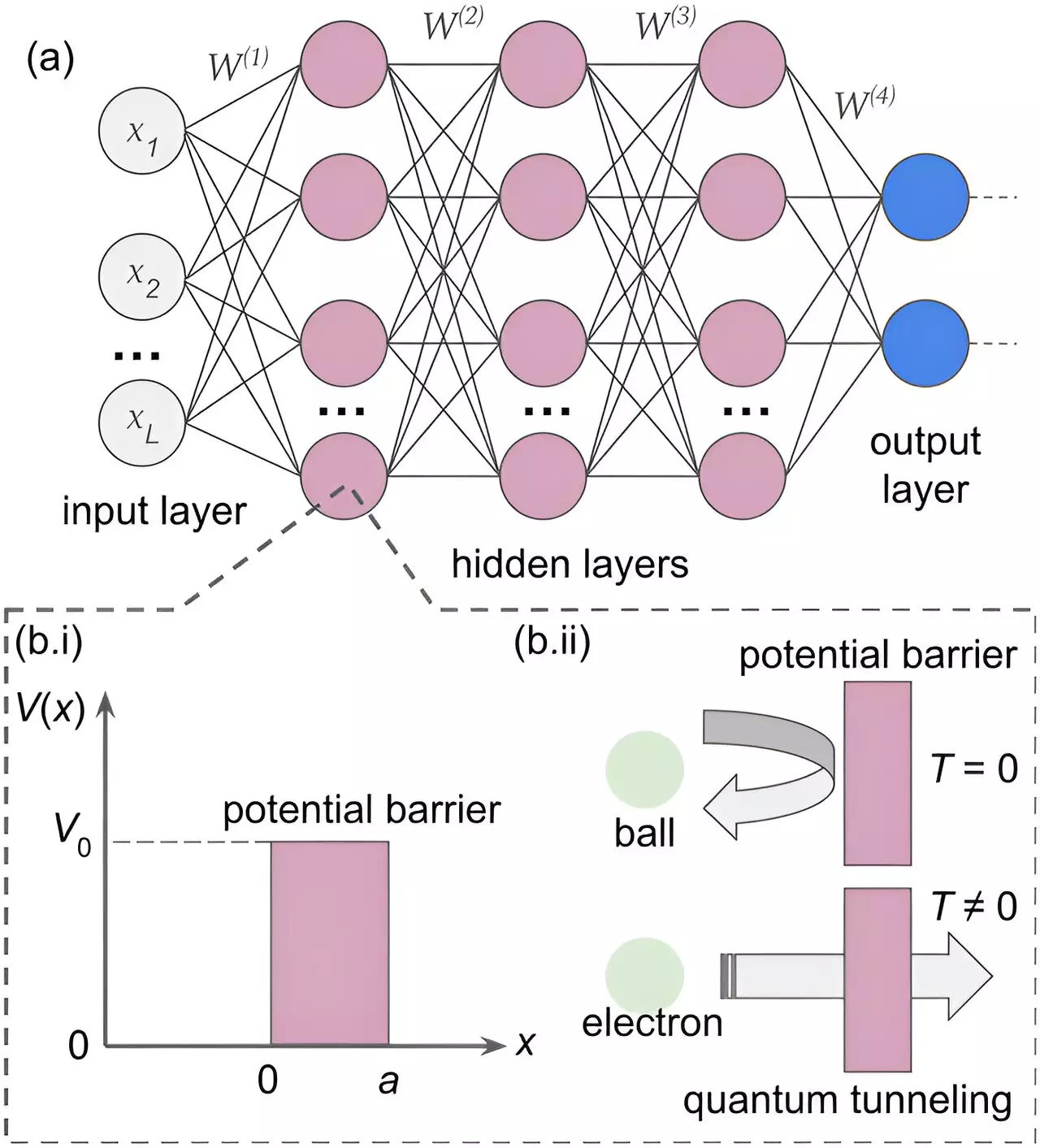
In the quest to emulate the human cognitive process, neural networks simulate the brain’s functions through layers of artificial neurons. These neurons, akin to their biological counterparts, classify and store data based on their relevance. By integrating concepts from quantum mechanics, particularly quantum tunneling, the neural network devised in this study exhibits a unique ability to navigate perception like the human brain. Quantum tunneling allows neurons to surpass barriers and activate even when conventional methods dictate otherwise, mirroring the versatile nature of human cognition.
The phenomenon of quantum tunneling, first elucidated in the early 20th century, revolutionized scientific understanding by explaining seemingly inexplicable natural occurrences such as radioactive decay. In contemporary times, the inadequacy of conventional theories in elucidating human behavior and decision-making has prompted exploration into quantum mechanics. The infusion of quantum effects into neural networks offers a novel perspective on understanding human cognition, transcending traditional limitations.
Quantum Effects in Neural Networks
By injecting quantum effects into the neural network’s operations, researchers aim to uncover the intricacies of human perception, especially when faced with ambiguous stimuli like optical illusions. Drawing parallels to Schrödinger’s cat, where quantum superposition manifests as simultaneous states, the neural network exhibits oscillatory behaviors in interpreting illusions. Unlike conventional networks, this quantum-inspired model captures the nuanced interplay between conflicting interpretations, mirroring the nuanced decision-making processes of the human brain.
Implications and Future Directions
In an era dominated by misinformation and manipulated media, understanding how our minds discern illusions and construct reality has never been more vital. Beyond optical illusions, the integration of quantum effects may hold the key to comprehending social behaviors and opinion radicalization in digital networks. The long-term prospects of quantum-powered AI extend to the realm of conscious robotics, heralding a new era of sentient machines. As research in this domain persists, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in understanding and replicating human cognition remains ripe for exploration.

Leave a Reply