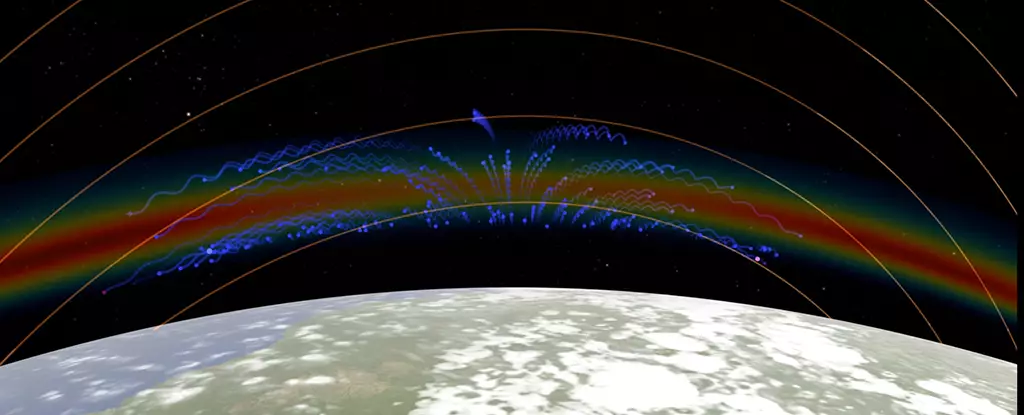
The ionosphere, a region of Earth’s atmosphere located between 48-965 kilometers above us, has recently been the subject of a fascinating discovery by NASA scientists. These researchers have identified peculiar shapes in this part of the atmosphere that could have significant implications for space weather forecasts and radio communications. While similar shapes have been observed in the past, the latest findings from the GOLD imaging instrument provide a clearer and more detailed view of these enigmatic formations.
One of the key factors at play in the formation of these shapes is the presence of plasma bands in the ionosphere. These bands are created when the atmosphere becomes electrically charged during the day, due to sunlight interacting with it. The charged particles in these bands are further influenced by Earth’s magnetic field, leading to the creation of crests and bubbles of plasma that give rise to the observed shapes. Previous studies have indicated that merging crests can form X shapes following solar storms and volcanic eruptions, but the data from this new study suggests that these shapes can also emerge during quieter periods, indicating the influence of more localized factors.
One of the puzzling aspects of the recent discovery is the appearance of C-shaped and reverse C-shaped bubbles in the plasma. While it is believed that winds on Earth play a role in shaping these bubbles, the close proximity of these C shapes, sometimes just a few hundred miles apart, hints at the involvement of additional factors such as wind shears or tornadoes. Despite being relatively rare, with only two instances observed by GOLD so far, these tightly packed C shapes have captured the curiosity of researchers who are keen to delve deeper into understanding their origins in the ionosphere.
Plasma in the ionosphere plays a crucial role in facilitating the transmission of radio waves over long distances, as well as supporting the functioning of GPS systems. Any disruptions in the ionosphere, like those caused by the unusual shapes detected by GOLD, could potentially affect vital communication and navigation infrastructure. By studying these phenomena in more detail, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of how radio and GPS technologies operate, and how they can be protected from the impact of atmospheric disturbances.
The recent findings regarding the mysterious shapes in the ionosphere highlight the complexity and intricacy of Earth’s atmosphere. As technology continues to advance and our capabilities for scientific research improve, we are able to uncover new phenomena and expand our knowledge of the world around us. The discoveries made by NASA’s GOLD imaging instrument are just one example of how innovative research methods are helping us gain deeper insights into the workings of our planet and the universe beyond. As we continue to explore and analyze the mysteries of the ionosphere, we can look forward to further revelations that will enhance our understanding of the dynamic forces at play in the Earth’s atmosphere.

Leave a Reply