In a groundbreaking study published in Nano-Micro Letters, a research team led by Prof. Meng Guowen, Prof. Han Fangming, Prof. Wei Bingqing, and Prof. Li Xiaoyan has developed high-density three-dimensional carbon tube nanoarray electrodes for line-filtering capacitors. This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize high-performance miniaturized filter devices, offering significant advantages over traditional aluminum electrolytic capacitors (AECs) and electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs).
Innovative Approach to Electrode Design
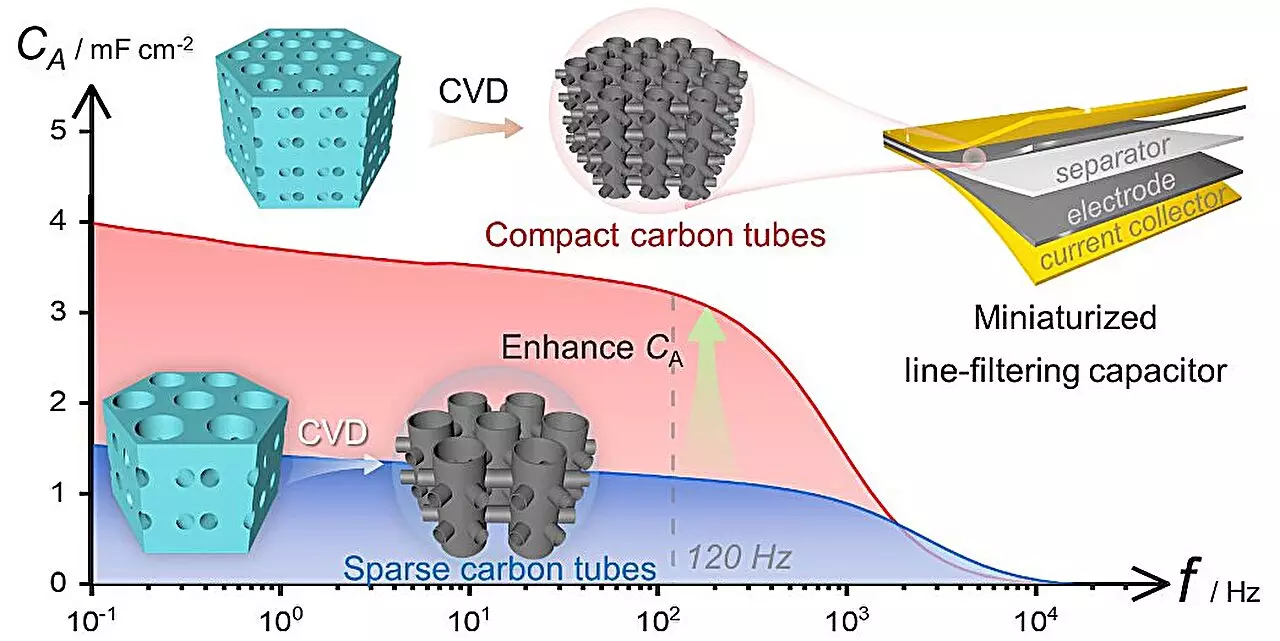
The research team focused on manipulating the pore structure of three-dimensional interconnected porous anodized aluminum oxide (3D-AAO) templates to create 3D compactly arranged carbon tube (3D-CACT) nanoarray electrodes. By tuning the vertical pore diameter of the templates and the inter-pore spacing, they were able to significantly increase the specific surface area of the electrodes. This optimization resulted in exceptional frequency response performance, with a phase angle of -80.2° at 120 Hz, ultra-low equivalent series resistance, and rapid resistance-capacitance time constant.
The 3D-CACT electrode-based device exhibited a specific areal capacitance at 120 Hz that far exceeded that of commercial AECs and previously reported EDLCs, highlighting its ability to facilitate efficient ion transport and offer abundant charge adsorption sites. Furthermore, the researchers demonstrated the scalability of their approach by connecting multiple sets of 3D-CACT-based EDLCs in series, extending the capacitors’ operating voltage without compromising their performance.
To showcase the practicality of their invention, the research team used 10 series-connected devices as filters to convert various alternating current inputs into smooth direct current signals. The filtering performance of the 3D-CACT nanoarray electrodes was comparable to commercial AECs, highlighting their potential for use in high-performance filter capacitors. This technology has the potential to advance miniaturized power systems and electronics, offering promising solutions for a wide range of applications.
Overall, the development of high-density 3D carbon tube nanoarray electrodes represents a significant advancement in the field of line-filtering capacitors. The innovative approach to electrode design, superior performance, scalability, practical applications, and future implications of this technology position it as a game-changer in the world of miniaturized filter devices. With further research and development, these electrodes have the potential to revolutionize the electronics industry and pave the way for more efficient and compact power systems.

Leave a Reply