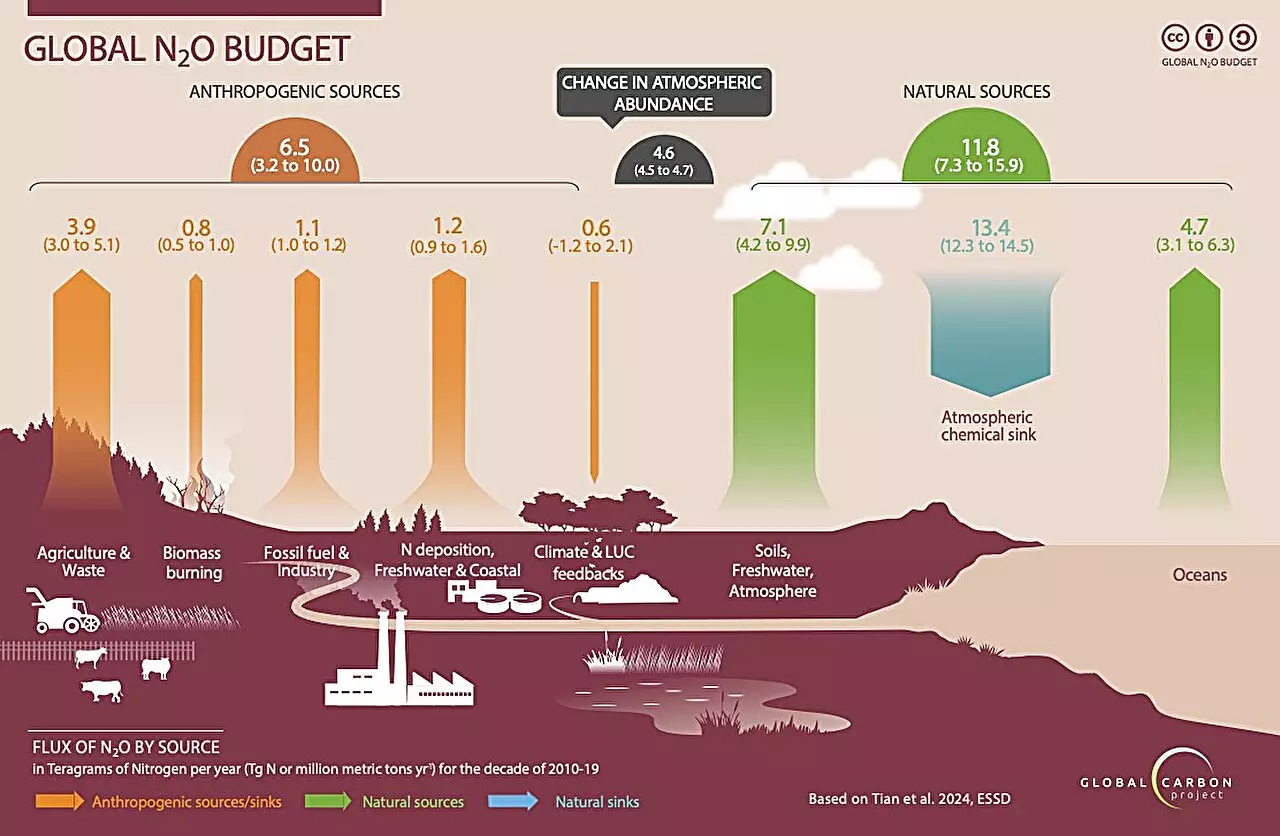
Nitrous oxide emissions, a greenhouse gas more potent than carbon dioxide or methane, have continued to rise without restraint from 1980 to 2020. The Global Carbon Project’s latest report revealed that over 10 million metric tons of nitrous oxide were released into the atmosphere primarily due to agricultural practices. Chemical fertilizers and animal waste used in farming contributed significantly to these emissions, making agriculture the leading source of human-driven nitrous oxide in the 2010s. The report highlighted the urgent need for emission reduction to curb global warming and its detrimental impacts on the environment.
The relentless flow of nitrous oxide into the atmosphere poses grave threats to the planet, depleting the ozone layer and exacerbating climate change. The report emphasized that the concentration of atmospheric nitrous oxide reached alarming levels in 2022, surpassing predictions and surpassing the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s estimates. This surge in nitrous oxide emissions is occurring when global greenhouse gas emissions should be declining rapidly, underscoring the critical need for immediate action to mitigate its effects.
The comprehensive study conducted by a team of 58 researchers from 55 organizations in 15 countries shed light on the escalating nitrous oxide emissions worldwide. By examining data from various economic activities contributing to nitrous oxide levels, the researchers identified the top 10 emission-producing countries. Despite some countries making strides in reducing emissions through policy implementations, the overall trend points to an alarming increase in nitrous oxide concentrations in the atmosphere.
The report stressed the importance of adopting sustainable agricultural practices to limit nitrous oxide emissions. By reducing the use of nitrogen fertilizers and animal waste, farmers can mitigate their contributions to greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution. The Global Carbon Project emphasized the necessity for more frequent assessments and enhanced inventories of emission sources and sinks to align with the goals of the Paris Agreement.
Addressing the rising dangers of nitrous oxide emissions requires immediate and concerted efforts from governments, businesses, and individuals worldwide. The urgency of the situation demands proactive measures to reduce emissions, protect the environment, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. By raising awareness, implementing sustainable practices, and fostering global cooperation, we can work towards a more sustainable future for our planet.

Leave a Reply