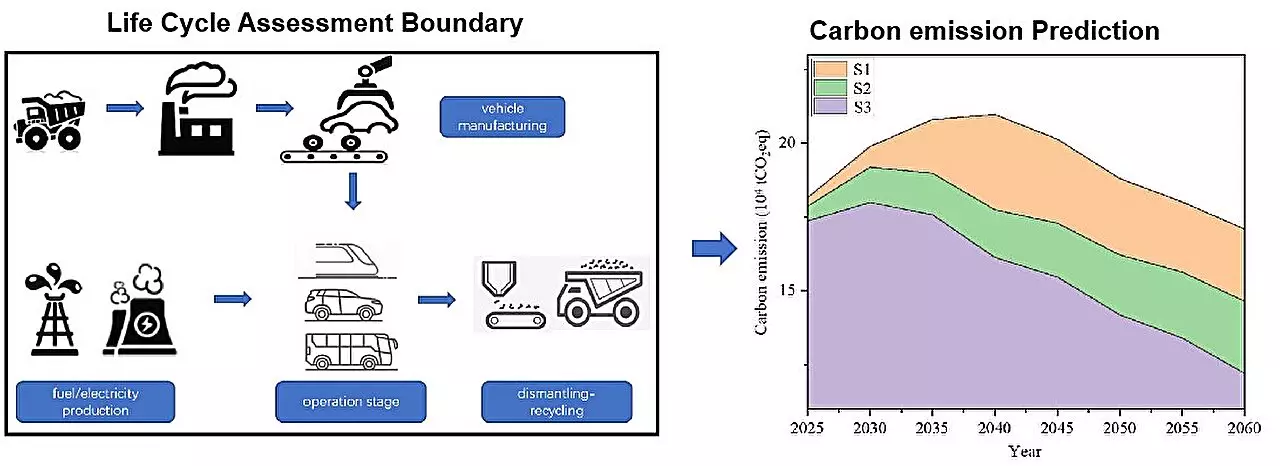
Transportation plays a significant role in global carbon emissions, ranking as the third largest contributor to the issue. In addressing this pressing concern, countries worldwide have been searching for effective solutions. High-speed railways (HSR) have emerged as a potential game-changer in intercity transportation due to their substantial electrification capabilities. However, the lack of relevant data highlighting the carbon reduction potential of high-speed rail travel and effective regulatory approaches for different transportation modes has hindered progress. In a recent study conducted by researchers from Beijing Jiaotong University, an in-depth analysis of the entire life cycle carbon emissions of vehicles sheds light on this critical matter.
Taking into account the complete life cycle of a product or tool, from resource extraction to its eventual return to nature, offers a more insightful perspective on its environmental impact. Lead author of the study, Lu Yintao, emphasizes the significance of assessing carbon emissions throughout the entire life cycle to determine a product’s environmental friendliness. By applying this approach to transportation, the researchers examined various modes of passenger travel, including private cars, buses, and railways, considering the multitude of energy sources consumed by each. This allowed for a deeper understanding of which transportation combinations are more effective in reducing carbon emissions during travel.
Traditionally, road transportation has been the primary choice for passenger travel. However, this study presents a contrasting viewpoint. Comparing the carbon emissions of HSR to private vehicles and buses, the findings reveal a substantial carbon emission reduction potential. High-speed rail travel demonstrates an impressive carbon intensity of only 24% to 32% when compared to private vehicles and 47% to 89% compared to buses. This significant disparity highlights the vital role that high-speed railways can play in reducing carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
Beyond its impact on carbon reduction in transportation, this study also provides valuable insights for vehicle manufacturers. The researchers’ findings offer guidance on the materials that manufacturers should prioritize for production, considering their significant implications for carbon reduction. By aligning production practices with sustainability goals, manufacturers can contribute to cleaner transportation options and the overall reduction of carbon emissions.
The study emphasizes that carbon emissions during transportation form a continuous process that significantly influences the entire life cycle of carbon emissions. Therefore, the researchers hope that their comprehensive analysis will serve as a valuable source of theoretical support for China’s ongoing carbon reduction efforts in the transportation sector. As countries worldwide strive to combat climate change and achieve carbon neutrality, the role of high-speed railways in reducing carbon emissions becomes increasingly pivotal.
As the world seeks innovative solutions to combat climate change, high-speed railways emerge as a beacon of hope in the transportation sector. With their high degree of electrification and remarkable carbon reduction potential, they present a promising future for intercity travel. The findings from this study shed light on the effectiveness of high-speed rail travel in reducing carbon emissions and provide critical insights for policymakers, vehicle manufacturers, and individuals alike. By embracing this more sustainable mode of transportation, nations can take significant strides towards a greener and more environmentally friendly future.

Leave a Reply